Transformer Routine Tests

Transformers are one of the most important electrical components, which play a vital role in power transmission and distribution systems. To ensure the proper functioning of transformers, routine tests are necessary to be carried out periodically. These tests help in detecting any faults or abnormalities in the transformer and prevent the occurrence of any damage or failure. In this blog, we will discuss the various routine tests (as listed below) performed on transformers, along with their methods of analysis.
- Winding Insulation Resistance Measurement
- Transformer Turns Ratio Test
- Vector Group Test
- Magnetic Balance Test
- Magnetizing Current Measurement
- Winding Resistance Measurement
Insulation Resistance Measurement
The insulation resistance of a transformer is measured to determine the condition of the insulation provided on the various conducting parts. This test is carried out by applying a DC voltage between the windings and the ground and measuring the resistance. The results of the test are compared with the manufacturer's specifications, and any deviation from the prescribed values is indicative of a fault in the insulation system.
Table : Insulation Resistance Readings
If the measured value is lower than the standard value, it indicates that the insulation system has a fault or weakness.
Transformer Turns Ratio Test
Turns ratio test is carried out on transformers to measure the ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to the number of turns in the secondary winding. The turns ratio is an essential parameter of a transformer as it determines the voltage transformation ratio between the primary and secondary windings.
During the turns ratio test, a low voltage AC supply is applied to the primary winding, and the induced voltage in the secondary winding is measured. The turns ratio is calculated by dividing the number of turns in the primary winding by the number of turns in the secondary winding.
Figure : Transformer Turns Ratio Test
The turns ratio test is critical because it ensures that the transformer is operating at the correct voltage level and that the voltage transformation ratio is within the specified limits. An incorrect turns ratio can result in a variety of problems, such as incorrect voltage levels, reduced efficiency, and even damage to the transformer or the power system.
Table : Transformer Turns Ration Readings
Additionally, the turns ratio test can be used to identify any possible manufacturing defects or faults in the transformer. If the turns ratio is found to be outside the specified limits, the transformer may need to be repaired or replaced.
In summary, the turns ratio test is an essential test carried out on transformers to ensure that they are operating at the correct voltage levels and that their voltage transformation ratio is within the specified limits. It is also useful in identifying any possible manufacturing defects or faults in the transformer.
Vector Group Test
Vector group test is carried out on transformers to determine their correct connections and to ensure that they are properly phased. The vector group of a transformer refers to the phase shift between the primary and secondary windings and is denoted by a combination of letters and numbers, such as Yyn0, Dyn11, etc.
The vector group test is important because it ensures that the transformer is properly connected to the power system and that its phase relationships are correct. Incorrect phasing or connection of a transformer can result in a variety of problems, such as reduced efficiency, increased losses, and even damage to the transformer or the power system.
Figure : Vector Group Test Setup
Additionally, the vector group test is useful in identifying any possible manufacturing defects or faults in the transformer. If the vector group is found to be incorrect, the transformer may need to be repaired or replaced.
Table : Vector Group Test Readings
To carry out this test, R phase of HV & LV winding terminals are shorted together. Three phase supplied is applied to HV winding at normal tap position. Voltage measurement is done as per above table. Following equations must be satisfied for test to be successful.
![]()
Figure : Vector Diagram for Vector Group Test
To analyze the result, the measured voltage is compared with the expected voltage, calculated based on the transformer's vector group. Any deviation from the expected value indicates a fault in the transformer's winding connection or phase displacement.
Magnetic Balance Test
Figure : Magnetic Balance Test
Magnetic balance test is carried out on transformers to ensure that the magnetic flux is evenly distributed across the transformer core. This test is particularly important in three-phase transformers where there is a possibility of uneven distribution of magnetic flux in the three phases.
The magnetic balance test involves measuring the voltage induced in each phase of the transformer while the other two phases are short-circuited. If the transformer is balanced, the induced voltages in each phase will be equal, indicating that the magnetic flux is evenly distributed.
Table : Magnetic Balance Readings
If there is an imbalance in the induced voltages, it could indicate a problem with the transformer core or winding. For example, a shorted turn in one phase of the winding can cause an imbalance in the magnetic flux and result in an unequal induced voltage. In such cases, corrective measures need to be taken to ensure that the transformer is repaired or replaced.
The magnetic balance test is an essential test carried out on transformers during their commissioning and maintenance to ensure their reliable and safe operation.
To analyze the result, the measured voltage is compared with the expected voltage, calculated based on the transformer's magnetic balance. Any deviation from the expected value indicates a fault in the transformer's winding connection or shorted turns.
Magnetizing Current Measurement
Magnetizing current is the current that is required to create the magnetic flux in the transformer's core. It is an important parameter to measure in a transformer because it is an indicator of the efficiency of the transformer.
If the magnetizing current is too high, it can lead to increased energy losses and reduced efficiency in the transformer. On the other hand, if the magnetizing current is too low, it may indicate a fault in the transformer or an incorrect design, which can also lead to reduced efficiency and other problems.
Figure : Magnetizing Current Test
Measuring the magnetizing current of a transformer allows engineers to ensure that the transformer is operating within its designed parameters and to detect any potential problems before they cause significant damage or failure. It is therefore an essential parameter to monitor and control during transformer operation.
The test involves applying a voltage to the primary winding of the transformer and measuring the current flowing through it.
Table : Magnetizing Current Readings
To analyze the result, the measured current is compared with the expected current, calculated based on the transformer's core losses. Any deviation from the expected value indicates a fault in the transformer's core, such as excessive core losses.
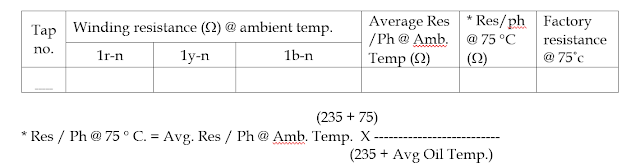
Winding Resistance Measurement
Winding resistance is an important parameter that affects the performance of a transformer. This test is carried out by measuring the resistance of the primary and secondary windings of the transformer. The resistance is measured with the help of a milli-ohmmeter or a bridge circuit.

Figure : Milli-Ohm Meter
Milli-Ohm Meter (Winding Resistance Meter) work on the concept of Ohm's law. Constant DC current is injected in winding under test. Current flowing through winding and voltage drop across winding terminals are measured and simple division of voltage by current will give winding resistance. Note down winding resistance of HV side on all tap positions, if possible. Also note down resistance of LV & TV windings.
Table : HV Winding Resistance Measurement
Table : LV Winding Resistance Measurement
Table : TV Winding Resistance Measurement
To analyze the result, the measured value is compared with the factory test report or commissioning report. If the measured value is higher, it indicates a fault in the winding, such as a connection looseness, short circuit or an open circuit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the routine tests carried out on transformers play a crucial role in ensuring their proper functioning and preventing any damage or failure. The insulation resistance measurement, winding resistance measurement, vector group test, magnetic balance test, and magnetizing current measurement are some of the critical tests that must be carried out periodically. The analysis of the test results is equally important, as it helps in detecting any faults or abnormalities in the transformer and taking appropriate corrective measures.