Smart Phone Controlled Home Automation Using Raspberry Pi
by bleuio in Circuits > Raspberry Pi
20 Views, 0 Favorites, 0 Comments
Smart Phone Controlled Home Automation Using Raspberry Pi
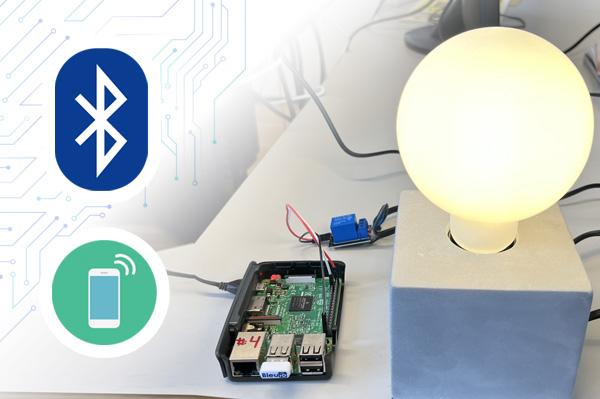
Home automation involves automating household environment equipment. To achieve that, we have created a smart bulb that can be controlled remotely using smart phone app. The aim of this project is to control different home appliances using smartphone at your home.
This example is showing how to control a GPIO pin on a RaspberryPi remotely from a smart phone (or another BleuIO Dongle).
Supplies
For this example we will need:
- A RaspberryPi
- A BleuIO Bluetooth USB Dongle (https://www.bleuio.com/)
- Our example python script (https://github.com/smart-sensor-devices-ab/bleuio_rpi_switch_example)
- A way to connect to the GPIO Pin (Like a 5V Relay and a Lightbulb)
WARNING – THIS PROJECT INVOLVES HIGH VOLTAGES THAT CAN CAUSE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. PLEASE TAKE ALL NECESSARY PRECAUTIONS, AND TURN OFF ALL POWER TO A CIRCUIT BEFORE WORKING ON IT.
Connecting the Relay
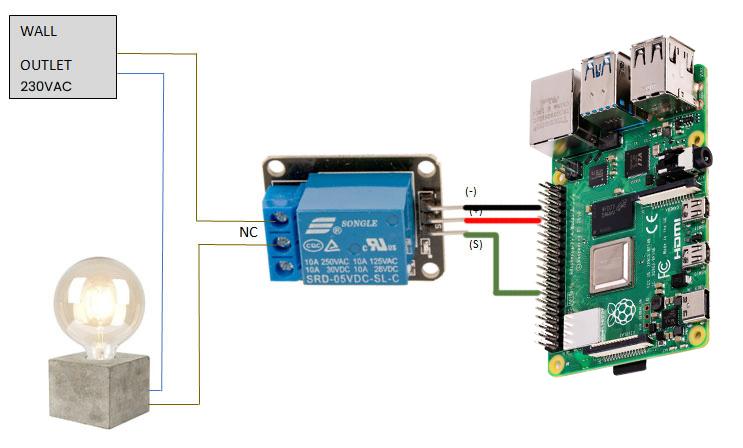
The image shows how to connect it with Raspberry Pi
Instructions for Bleuio_rpi_switch_example.py
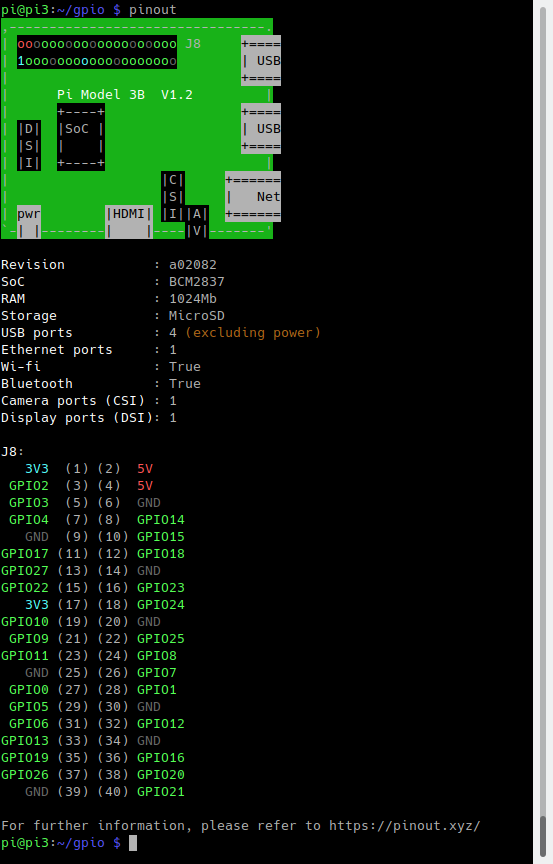
- Connect the BleuIO Dongle to your RaspberryPi.
- Edit the variable ‘switch’ in the script to the GPIO pin you want to use. (You can use the command pinout to get a graphical view showing you the GPIO pins for the board)
- Finally just run python script and and use your phone to connect to the BleuIO Dongle and send on/off messages to controll the GPIO!
Instructions for Connecting to the BleuIO From Mobile
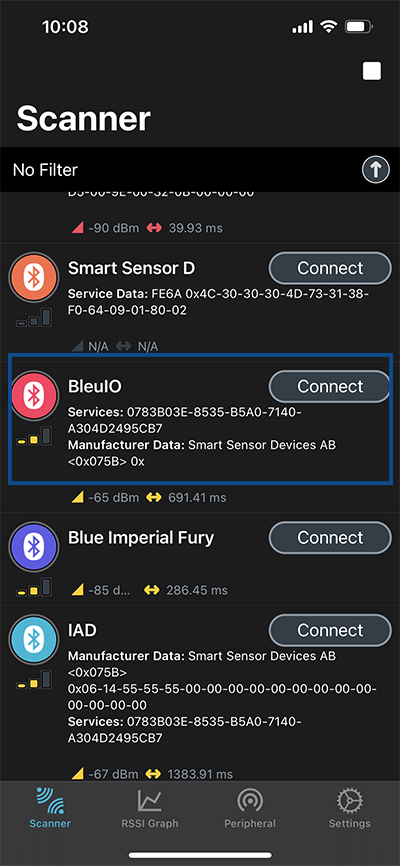
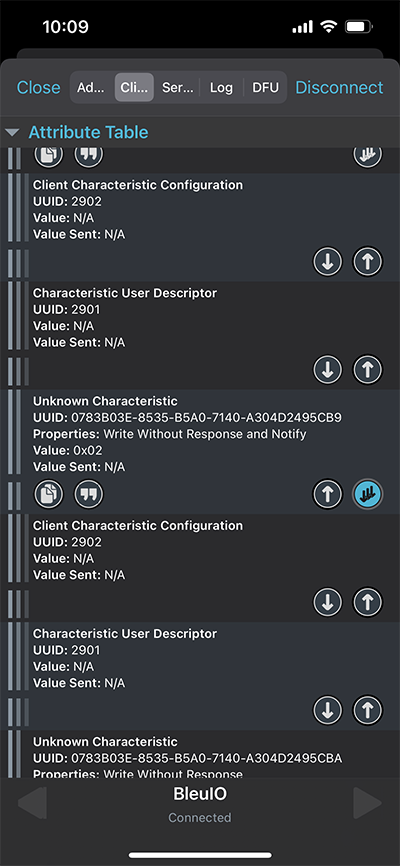
- Download a BLE scanning App that can connect and read/write to a device. (Like nRFConnect or BLEScanner)
- Android, IOS
- Look for the dongle, it will be advertising as ‘BleuIO’.
- Connect to the BleuIO Dongle.
- To enable BleuIO to recieve commands you must first write 0x01 to the Flow Control characteristic (UUID: 0783b03e-8535-b5a0-7140-a304d2495cb9)
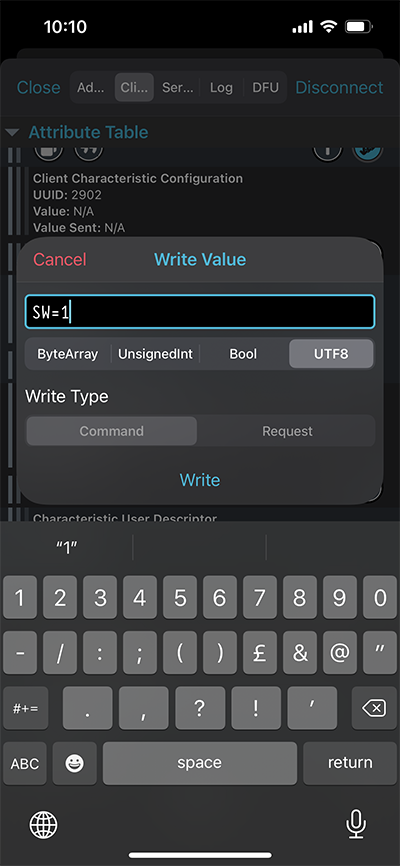
- Now you can write to the Server RX Data characteristic (UUID: 0783b03e-8535-b5a0-7140-a304d2495cba) to control the GPIO.
- “SW=1” for ON
- “SW=0” for OFF
The Script
Here is the python script that receives the messages from smart phone app and helps control the light.
#!/usr/bin/python3# Copyright 2022 Smart Sensor Devices in Sweden AB## Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"),# to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense,# and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.## THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,# WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.import timeimport serial.tools.list_portsimport serialimport RPi.GPIO as ioswitch = 7 # Edit this to suit your setup! (7 = GPIO 04), use command pinout to graphically show you the GPIO pins for the boardio.setmode(io.BOARD)io.setup(switch, io.OUT)master_array = []index = 1dongle_port = ""print("\nWelcome to BleuIO RaspberryPi Switch Example!\n")print("\nPlease insert dongle...")try: while len(master_array) == 0: m_ports = serial.tools.list_ports.comports(include_links=False) for port in m_ports: if str(port.hwid).__contains__("VID:PID=2DCF"): master = port.device + " " + port.hwid if master.__contains__("VID:PID=2DCF:6002"): print("Found dongle in port: %s" % port.device) master_array.append(master) dongle_port = port break for dongle in master_array: print("\nConnecting to BleuIO @ %s\n" % dongle) time.sleep(0.5) dongle_conn = serial.Serial( dongle_port.device, 115200, timeout=1, ) if not dongle_conn.is_open: dongle_conn.open() print("Starting Advertising...") dongle_conn.write("AT+GAPDISCONNECTALL\rAT+DUAL\rAT+ADVSTART\rATI\r".encode()) read_tries = 0 dongle_resp = "" while read_tries < 20: dongle_resp = dongle_conn.readline().decode() if "Not Advertising" in dongle_resp: dongle_conn.write("AT+ADVSTART\r") if b"Advertising\r\n" in dongle_resp.encode(): break read_tries += 1 time.sleep(0.01) if dongle_resp: print("BleuIO is %s" % dongle_resp) else: print("ERROR! No response...") exit() print( "Going into loop, waiting for signal to turn switch on/off...\n(Press Ctrl+C to abort)" ) while True: try: dongle_resp = dongle_conn.readline().decode() if "SW=0" in dongle_resp: print("Turn Switch off!") io.output(switch, io.LOW) if "SW=1" in dongle_resp: print("Turn Switch on!") io.output(switch, io.HIGH) except KeyboardInterrupt: if dongle_conn.is_open: dongle_conn.write("AT+GAPDISCONNECTALL\rAT+ADVSTOP\r".encode()) dongle_conn.close() io.cleanup() print("\nBye!") exit()except Exception as e: print("(ERROR: %s)" % (e))Output
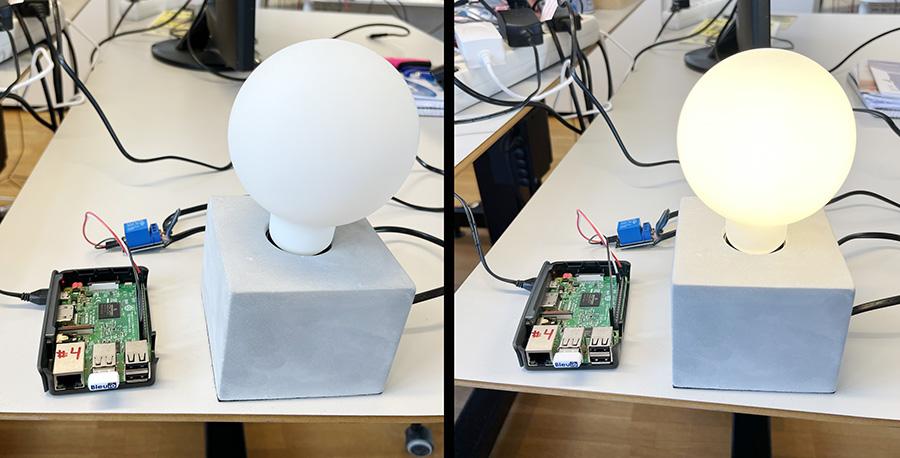
We have tested the script using nRFConnect app from both IOS and Android phone to turn on/off the light bulb. Here is the output of this project.