Smart AC Remote


Smart AC Remote
Tiny ESP8266 based remote to control your home Air Conditioner when your physical remote run out of battery.
This repository contains the code for an AC remote control using an ESP8266 microcontroller. It allows you to control an AC unit remotely through a web interface.
USP
- There are numerous solutions available for Arduino or ESP8266 based SoCs, but many of them lack practicality as retail universal remotes.
- An amplifier circuit has be implemented to enable control from any location within the room.
- If you have concerns about proprietary code and foreign servers, this solution can be particularly useful.
- The universal user interface (UI) is highly adaptable and can be customized to meet specific requirements.
- It is a highly cost-effective and straightforward solution to construct.
- The solution does not require any third-party services as it is self-hosted on the ESP8266 device.
- Multiple remotes can be created and added to the mobile homescreen using the "Add to Homescreen" button in the browser.
Supplies
Hardware Requirements
To use this code, you will need the following hardware:
- ESP8266 microcontroller (Node MCU or Wemos D1 Mini)
- 220 Ohm Resistor
- Transistor - NPN BC337
- IR LED (950nm)
- AC unit compatible with the ir_Coolix library (Midea or Carrier AC Unit -> Remote : RG56N/R3 and RG56CMI-WP2)
Libraries Used
The following Arduino libraries are used in this project:
- Arduino
- ArduinoJson
- ESP8266WiFi
- WiFiClient
- ESP8266WebServer
- ESP8266mDNS
- IRremoteESP8266
- ir_Coolix
Make sure to install these libraries in your Arduino IDE before compiling and uploading the code.
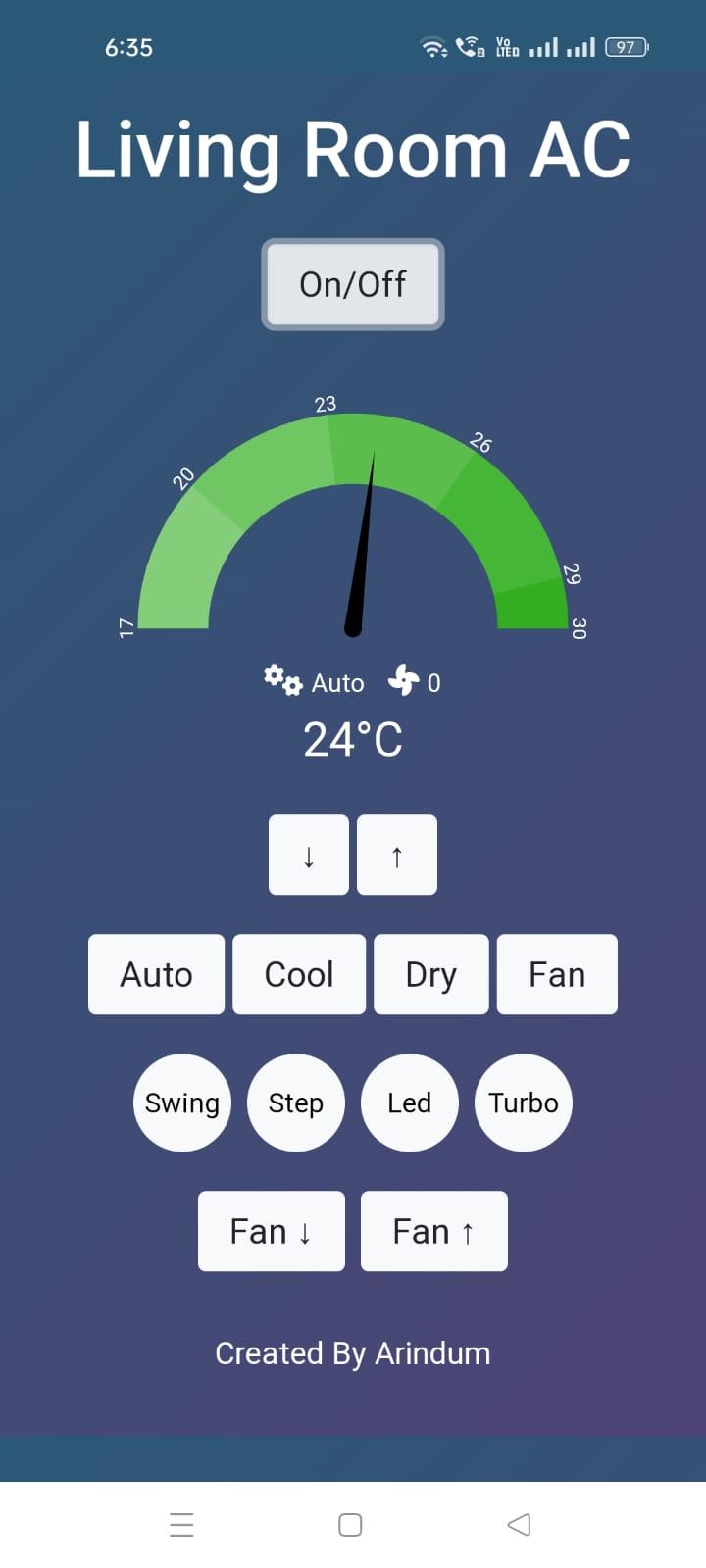
Usage
- Once the code is uploaded, the ESP8266 will connect to the Wi-Fi network and obtain an IP address.
- Access the remote control interface by navigating to http://<IP_ADDRESS>/index.html in a web browser, where <IP_ADDRESS> is the IP address assigned to the ESP8266.
- The web interface provides buttons and controls for various AC functions, including power on/off, mode selection, fan speed, temperature adjustment, and extra features like swing, step, turbo, and LED control.
- Clicking on the buttons will send the corresponding commands to the AC unit via IR signals.
- The current status of the AC (power, mode, fan speed, temperature) is displayed on the web interface.
- You can also retrieve the current AC data in JSON format by accessing http://<IP_ADDRESS>/getdata.
API Endpoints
The following API endpoints are available:
- /getdata: Returns the current AC data in JSON format.
- /togglePower?power=<true/false>: Toggles the power state of the AC unit. Pass power=true to turn on and power=false to turn off.
- /toggleMode?mode=<mode_value>: Changes the mode of the AC unit. Available mode values are Auto, Cool, Dry, and Fan.
- /toggleFan?fan=<fan_value>: Changes the fan speed of the AC unit. Available fan values are 0 (Auto), 1 (Min), 2 (Medium), and 3 (Max).
- /toggleTemp?temp=<temperature_value>: Changes the temperature of the AC unit. Provide the desired temperature value within the range of 17 to 30 degrees Celsius.
- /toggleExtra?extra=<extra_value>: Toggles extra features of the AC unit. Available extra values are Led, Turbo, Swing, and Step. Note: Replace <IP_ADDRESS> in the API endpoints with the actual IP address assigned to the ESP8266.
Credits
This project uses the following libraries:
- ArduinoJson: https://arduinojson.org/
- IRremoteESP8266: https://github.com/crankyoldgit/IRremoteESP8266
- ir_Coolix: https://github.com/z3t0/Arduino-IRremote
License
This code is released under the MIT License. Feel free to modify and use this code according to your needs. Contributions and improvements are always welcome! For more information and updates, visit the project repository.