How to Quickly Test and Diagnose a Two Way Radio Transmitter
by RadioManFran in Circuits > Wireless
8616 Views, 16 Favorites, 0 Comments
How to Quickly Test and Diagnose a Two Way Radio Transmitter
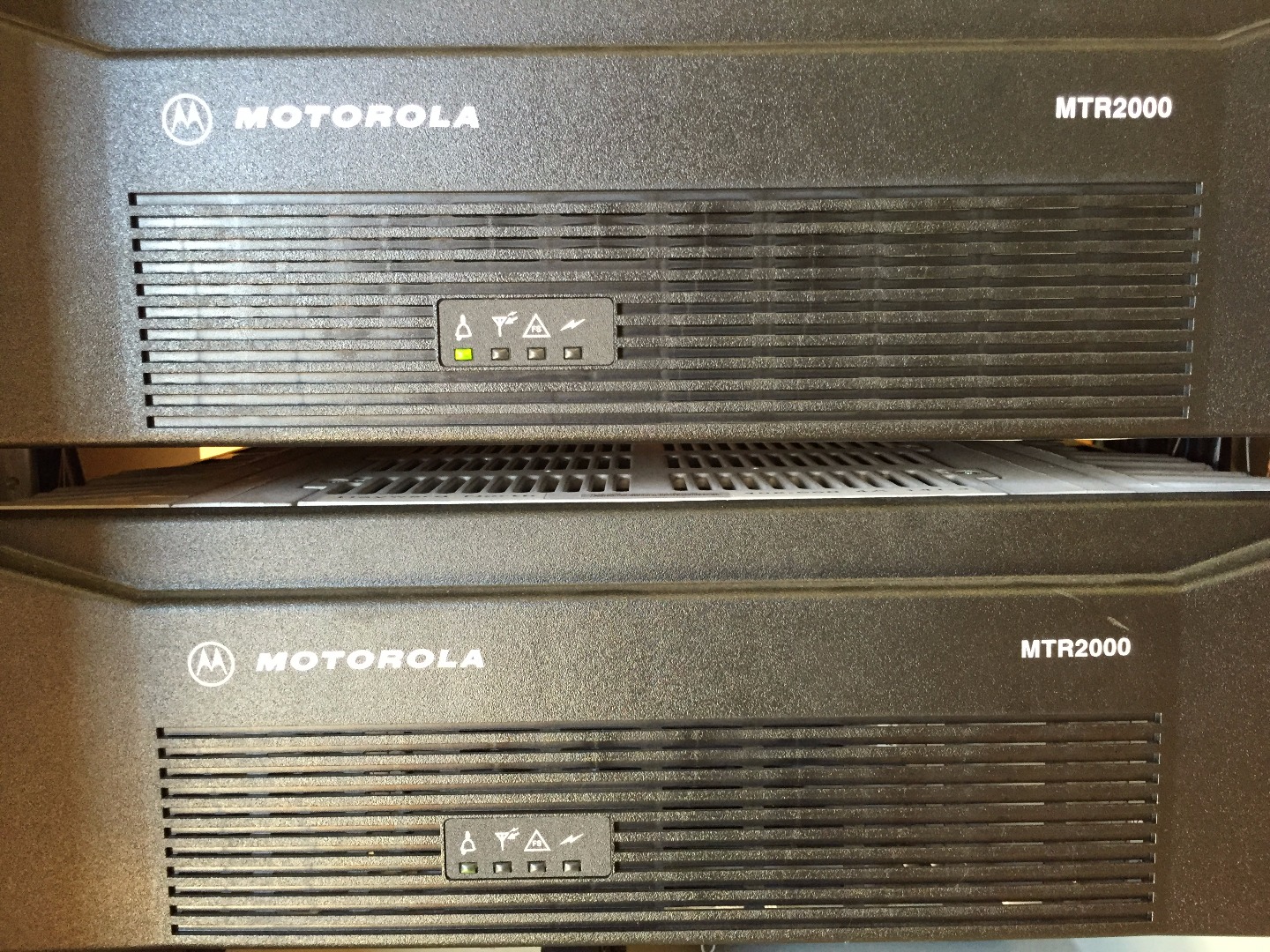

In this skill building exercise you will be shown how to simply and quickly diagnose the basic condition of a two way radio transmitter. Using a Bird Watt Meter, you will be able to get an idea if the transmitter is generating RF power at the desired levels and if there may be an issue with the antenna and feed line connecting to the transmitter. In this demonstration we are using a Motorola VHF MTR 2000 base station (transmitter) and a standard Motorola mobile microphone to key up the base station.
Equipment Needed
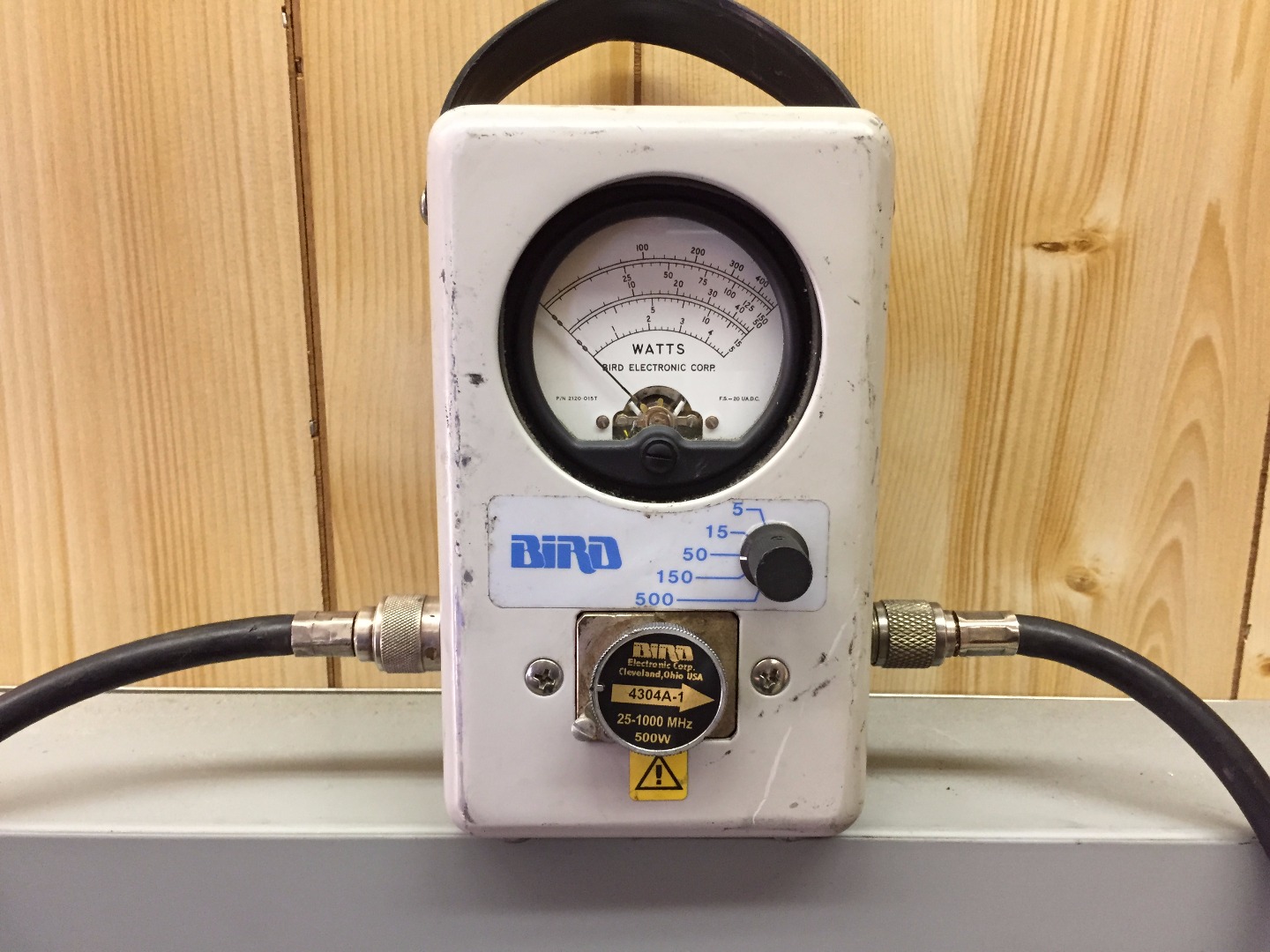




- Directional Watt Meter
- RG 8 Coax Cable Jumper with a Male N Type connector on one end and one male PL-259 connector on the other end
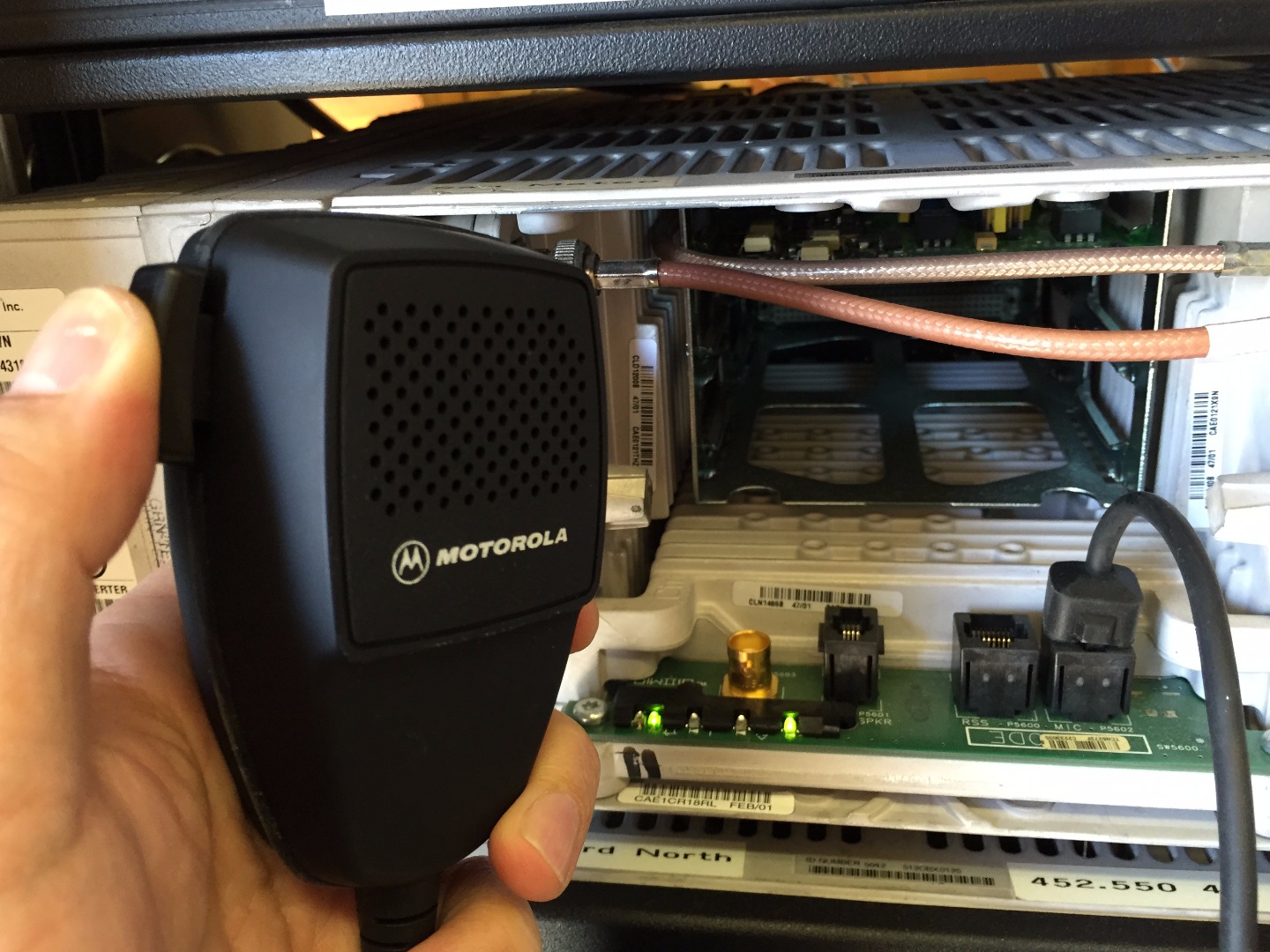
- Microphone or PTT (Push to Talk) accessory to key up radio
Connect Male N Type Jumper From Watt Meter Connection (left Side of Watt Meter in Picture) to Antenna Port on the Back Side of the Radio Transmitter (center Black RG 8 Cable in Second Picture)
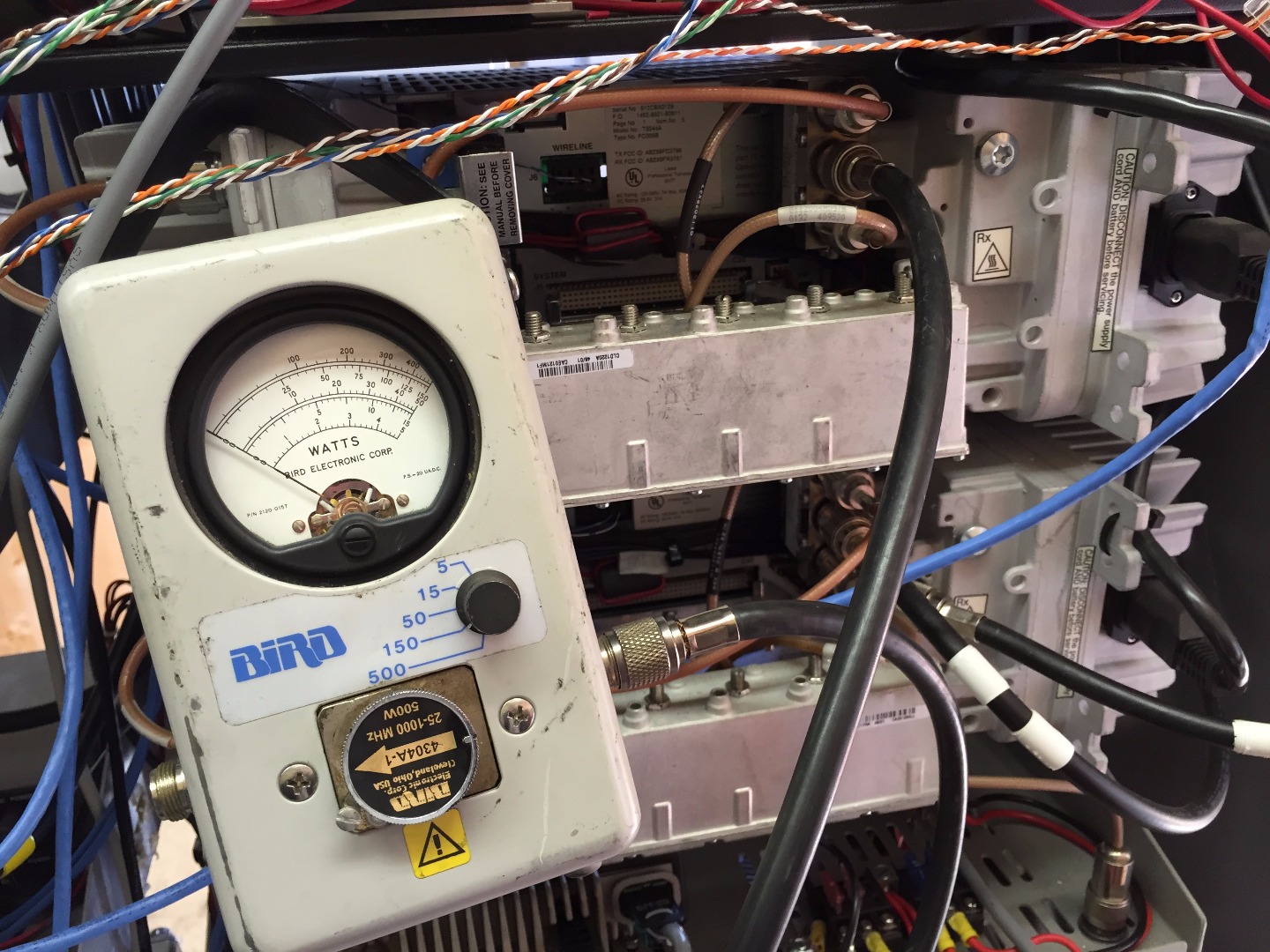
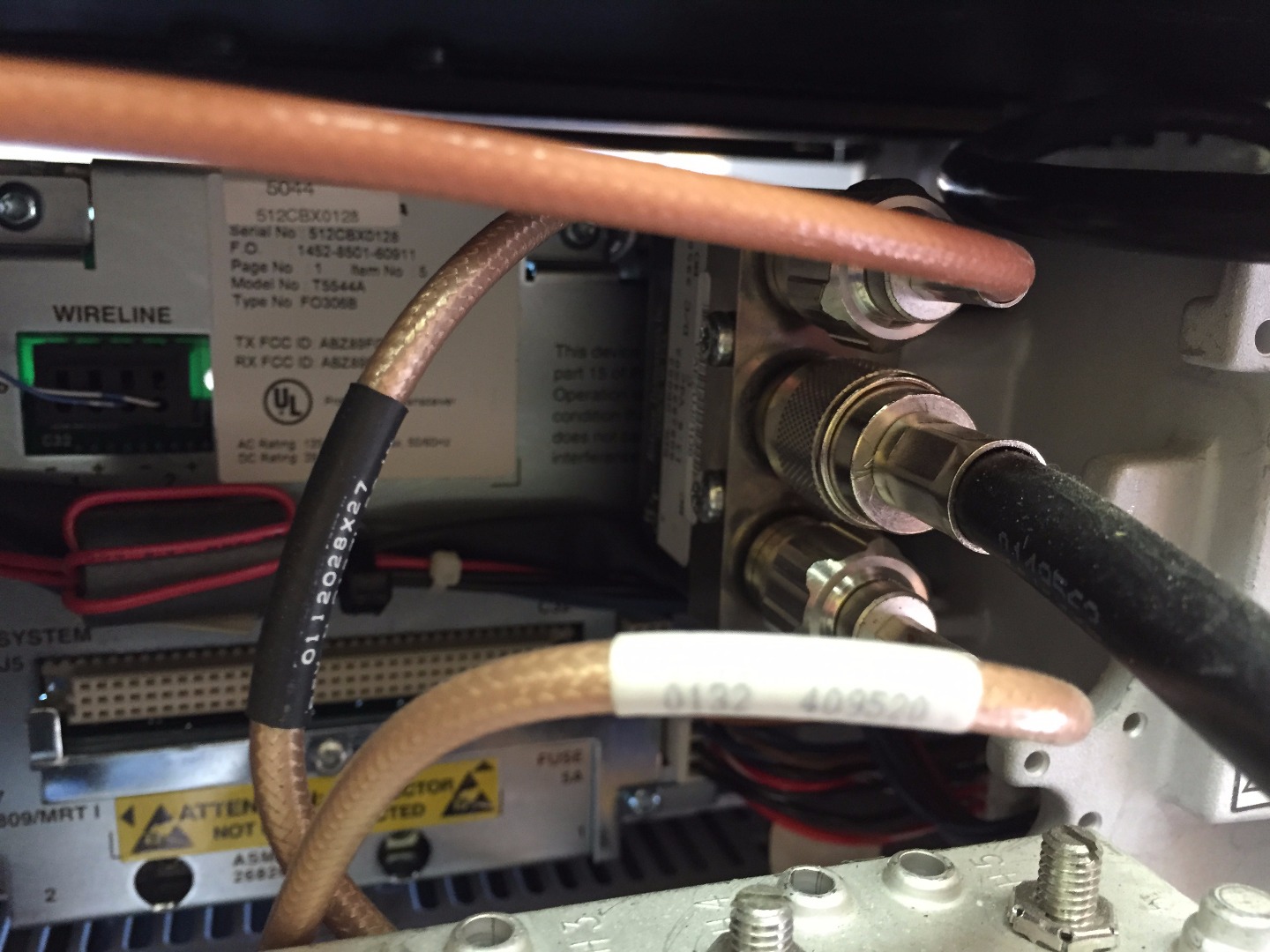
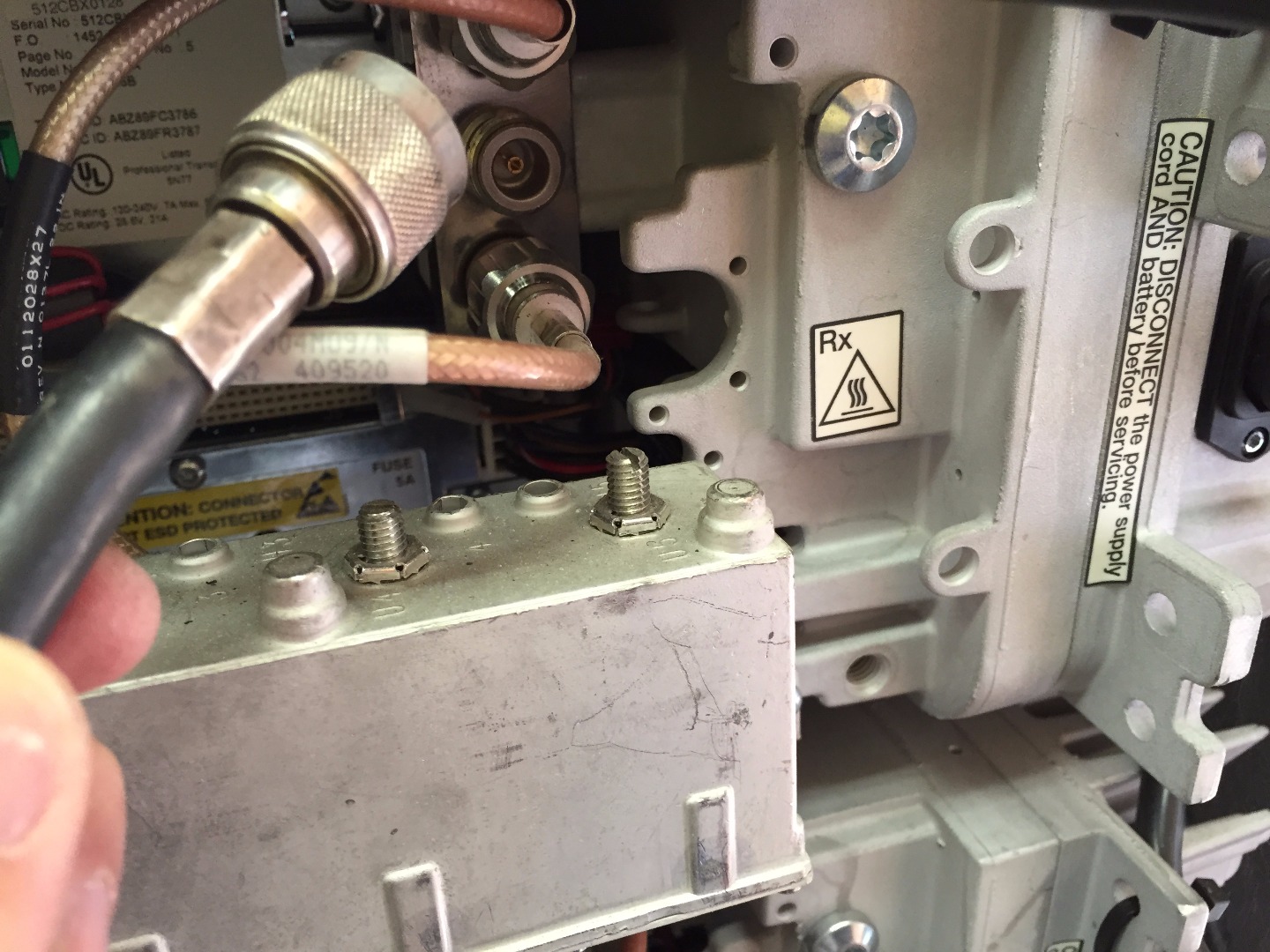
Connect Previously Removed RG 8 Antenna Cable From Radio Transmitter to Open N Type Port on the Watt Meter.
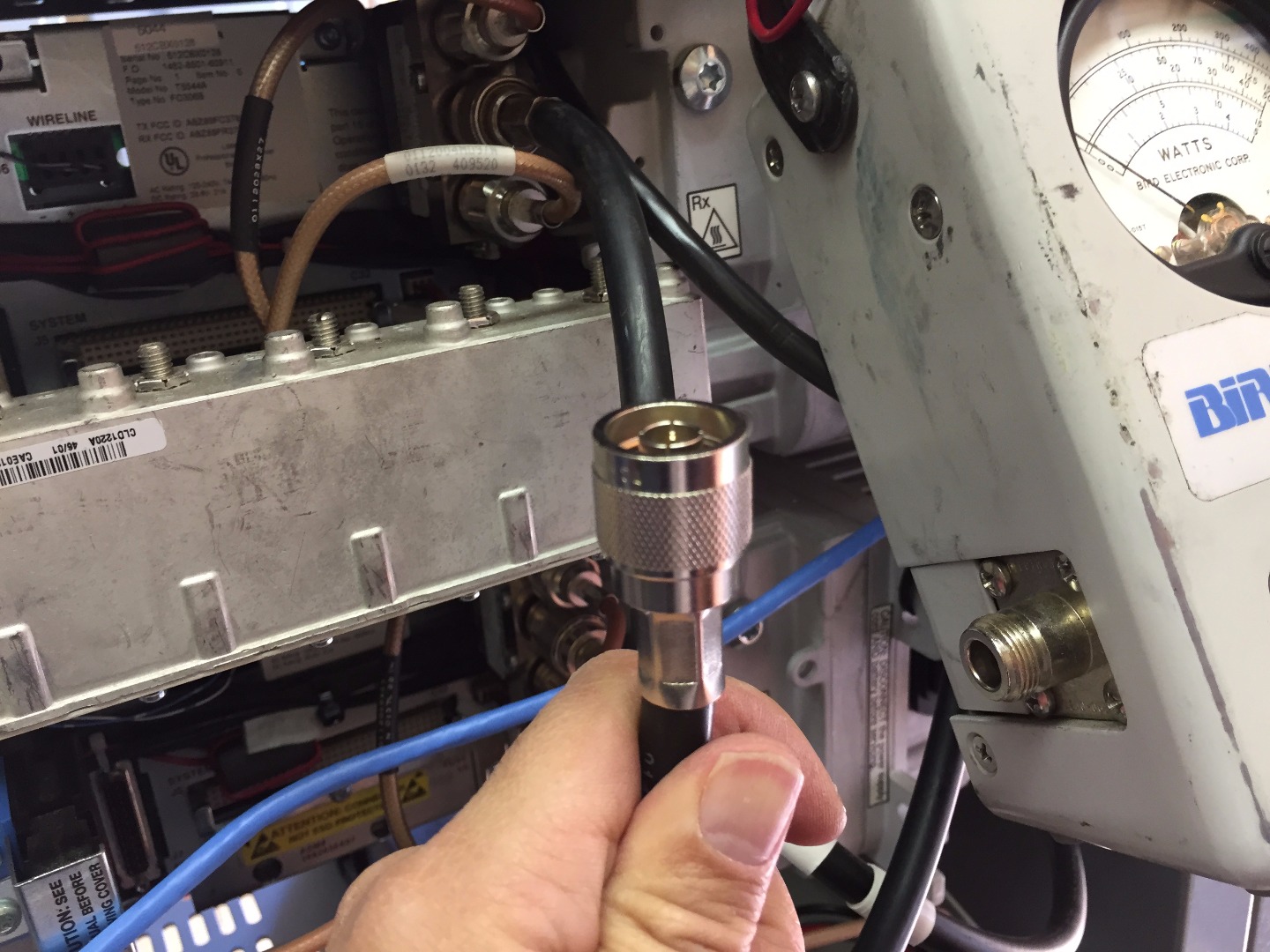

Testing for Foward Power From Radio
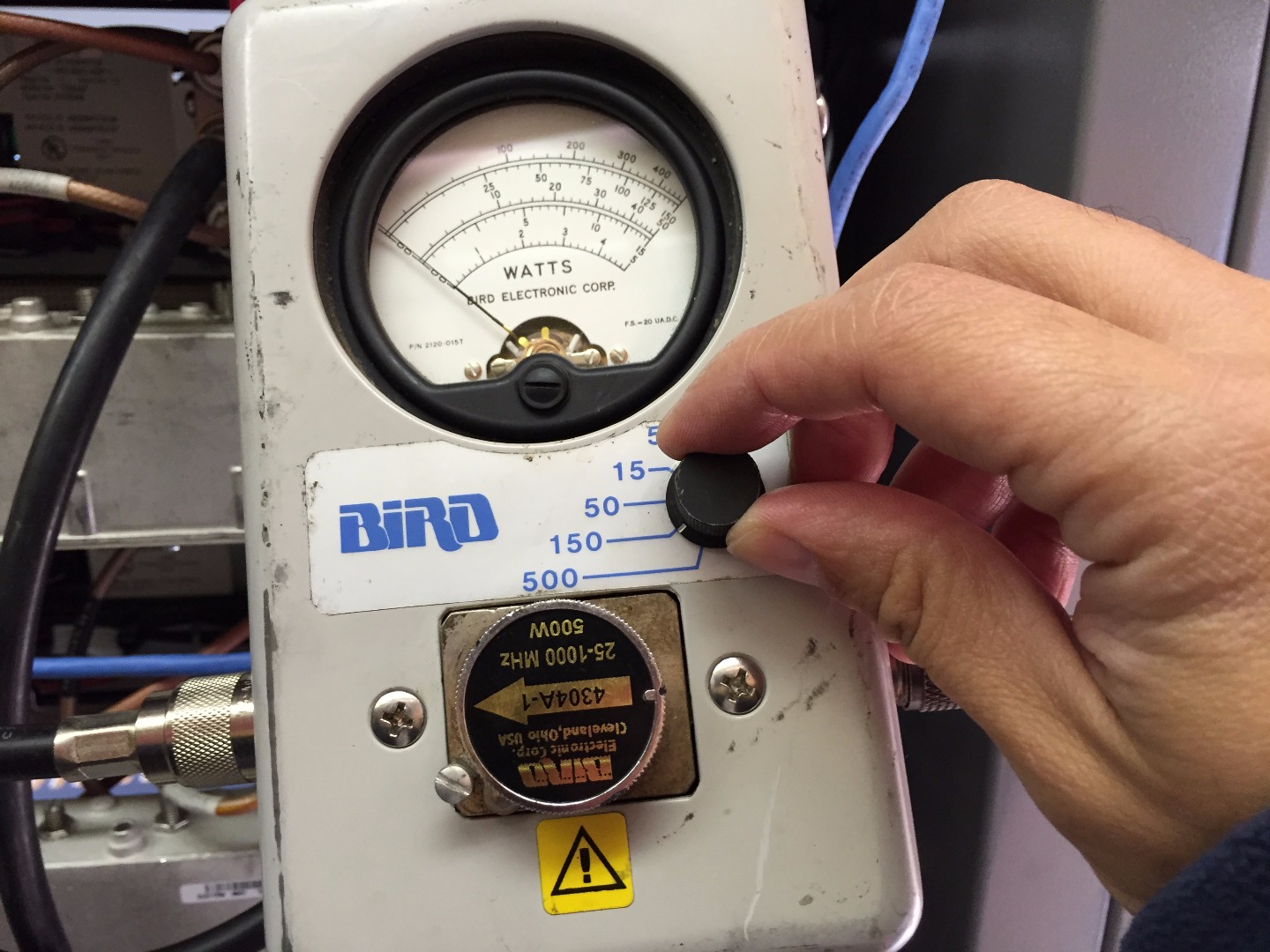
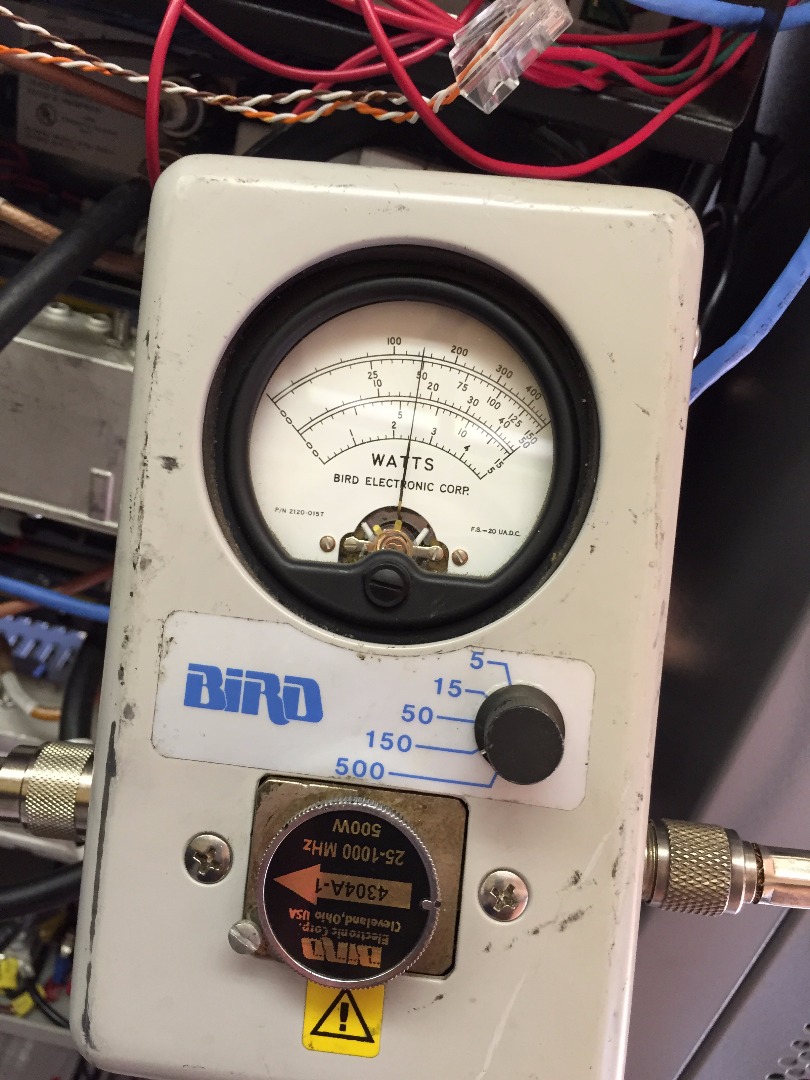
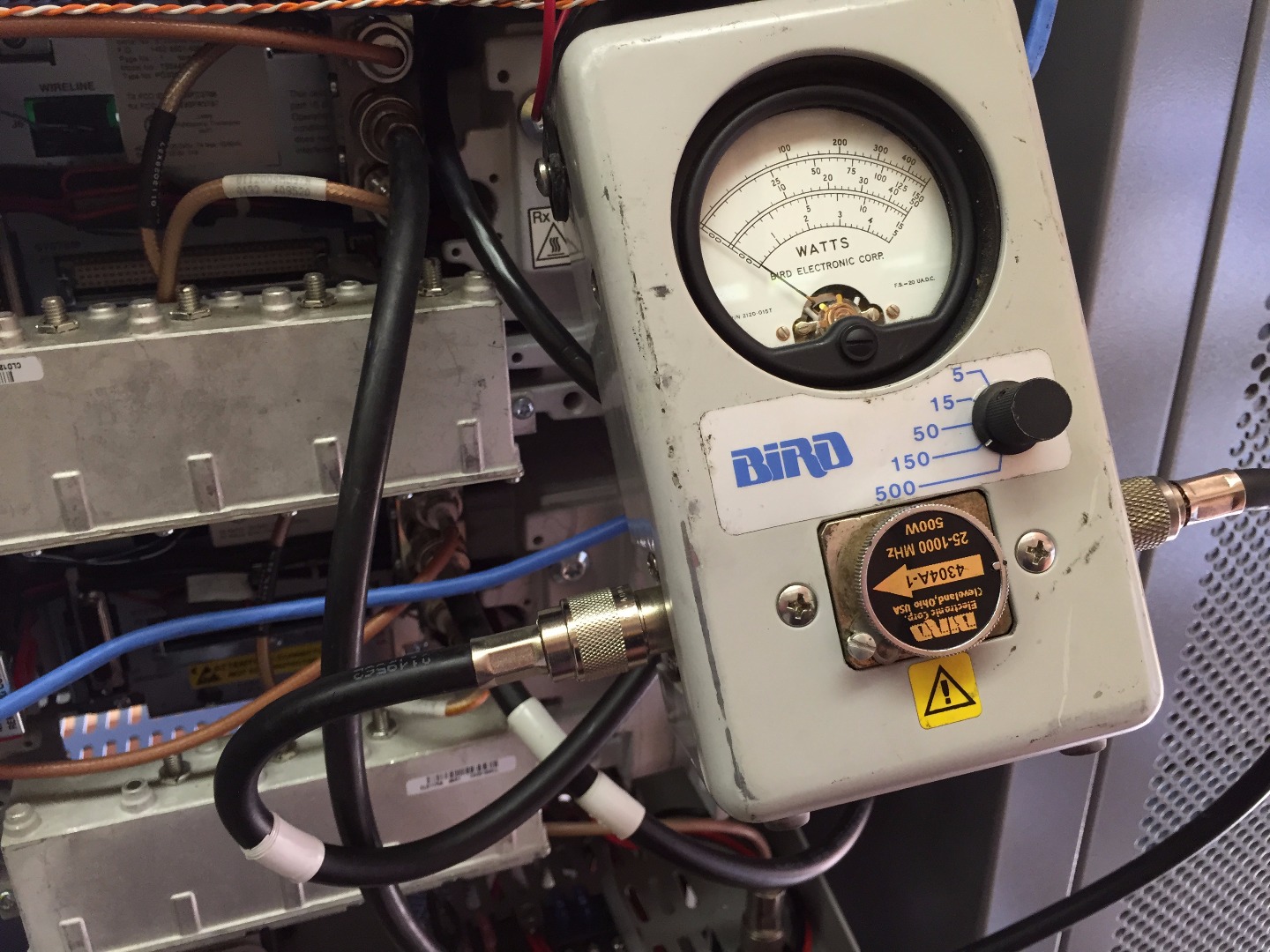



- Set watt meter needle range to 150 watts
- Rotate arrow dial pointing out towards the radio antenna (visualize the flow of RF energy coming out of transmitter thru the feed line coax cable to the antenna, we want the arrow to point in that direction)
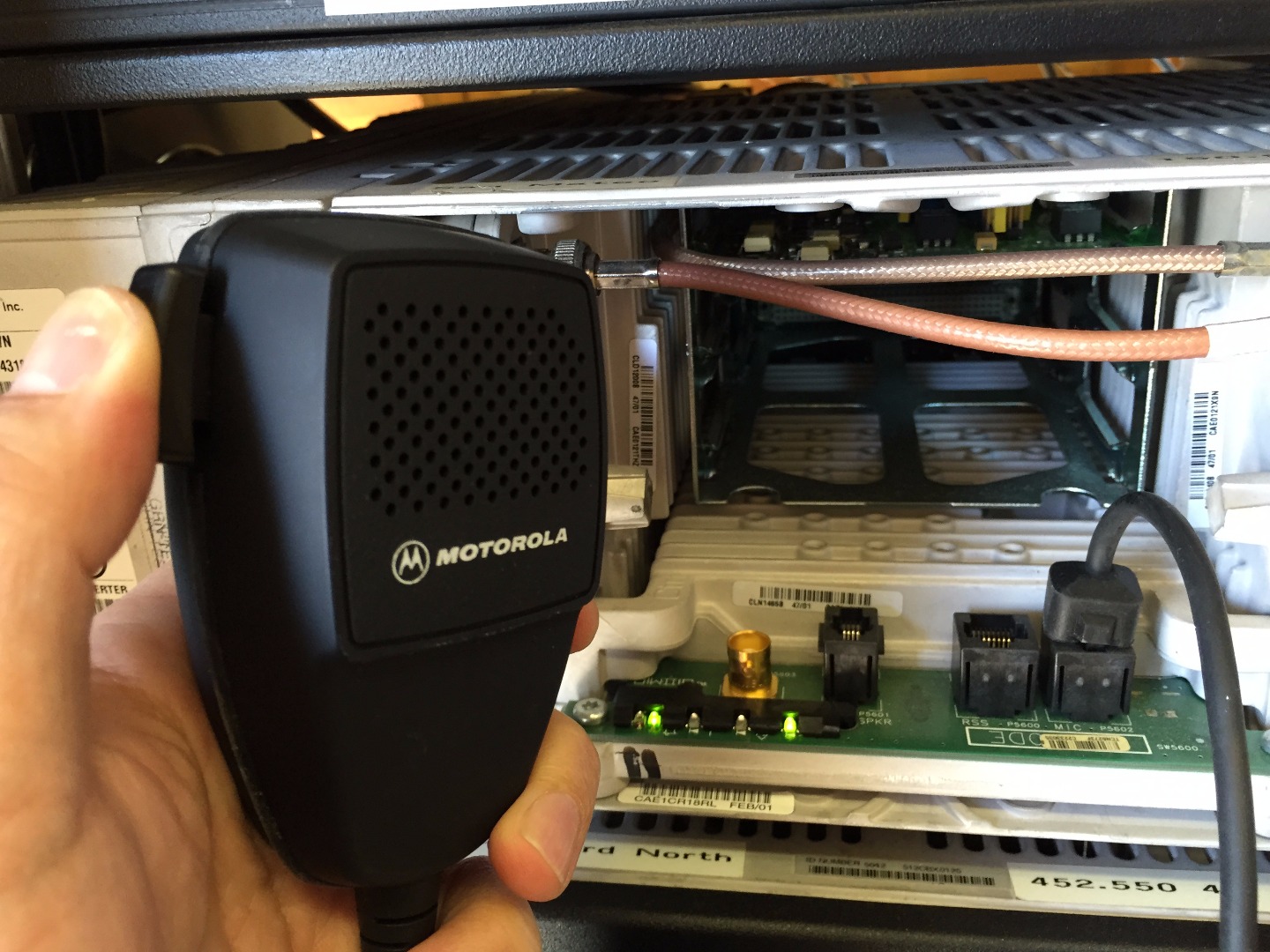
- Plug in microphone or PTT device into transmitter modular audio jack
- Key up radio
- Take note of wattage measurements
The watt meter will display the RF power produced by the radio when keyed up. One can immediately determine if there is an issue with the radio's power amplifier if the measurement is less than the specified or programmed transmit power out level. In this particular case the watt meter is measuring 50 watts out of the transmitter, which is the power level that the transmitter is expected to generate.
Testing for Reflected Power
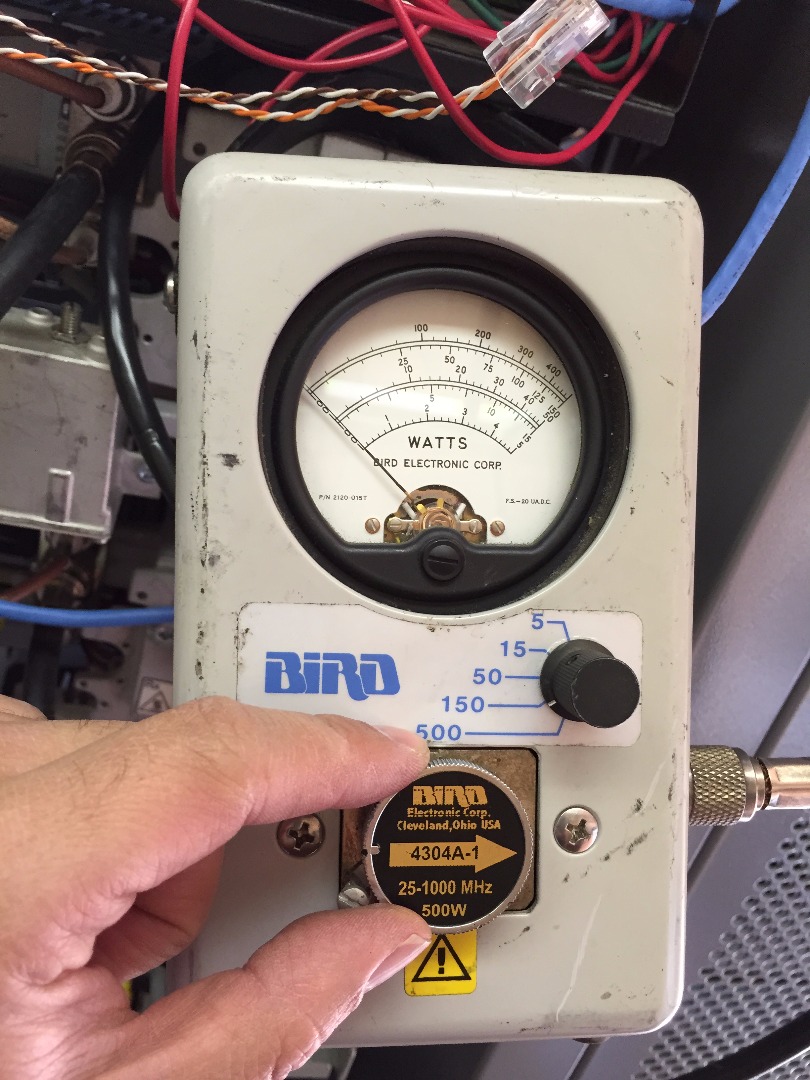
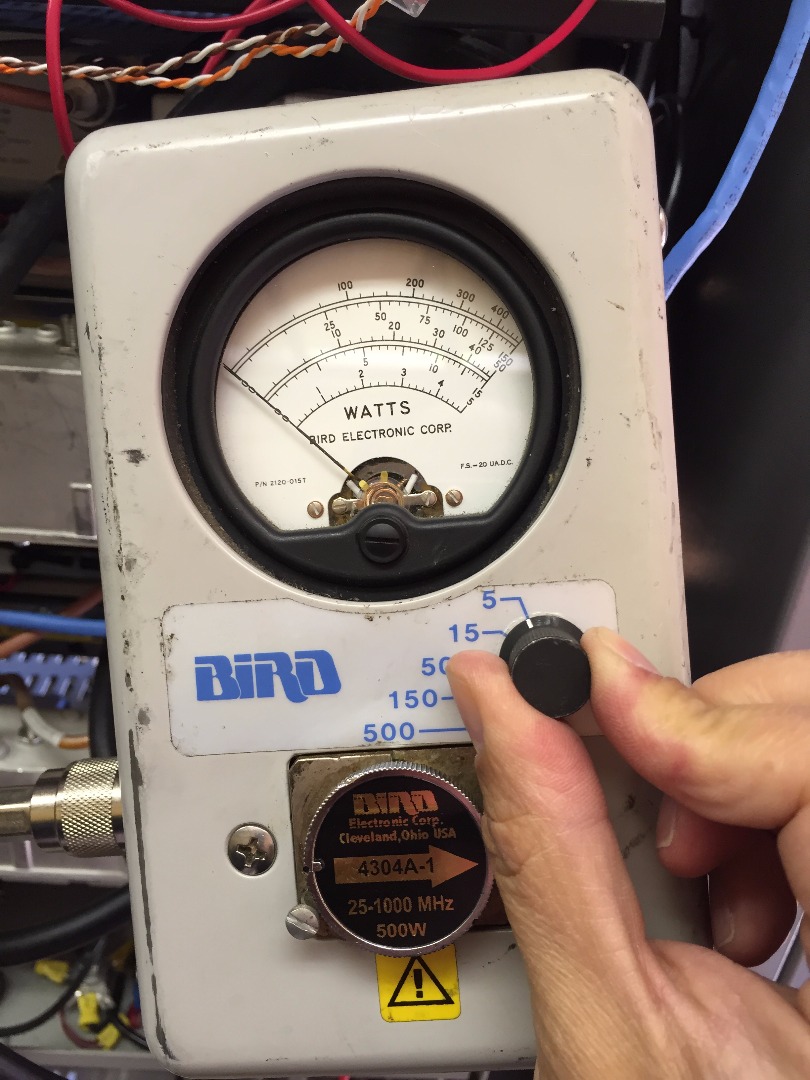




Set watt meter needle range to 5 watts
- Connect RG 8 Jumper to radio by repeating Steps 2 and 3
-
Rotate arrow dial pointing the opposite towards the radio transmitter (imagine the arrow going the opposite direction of the flow of RF power coming out of the radio, thru the coax feed line and towards the antenna)
-
Key up radio
-
Take note of wattage measurements
The watt meter will display the reflected RF power produced by the radio when it is keyed up. The wattage measurement is the amount RF power out reflected back to the transmitter from the antenna and feed line. In general a measurement of 1.5 watts or less is good. Any measurement higher than 1.5 watts indicates a possible issue with the antenna or coax feed line to antenna. This particular radio transmitter is measuring 1.2 watts reflected power which is acceptable. In this situation the radio transmitter is generating RF power that is flowing through the feed line to the antenna and ultimately transmitting out efficiently with little reflective power coming back.