How to Make a Business Model Canvas
by mgustin12 in Workshop > Organizing
86897 Views, 27 Favorites, 0 Comments
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
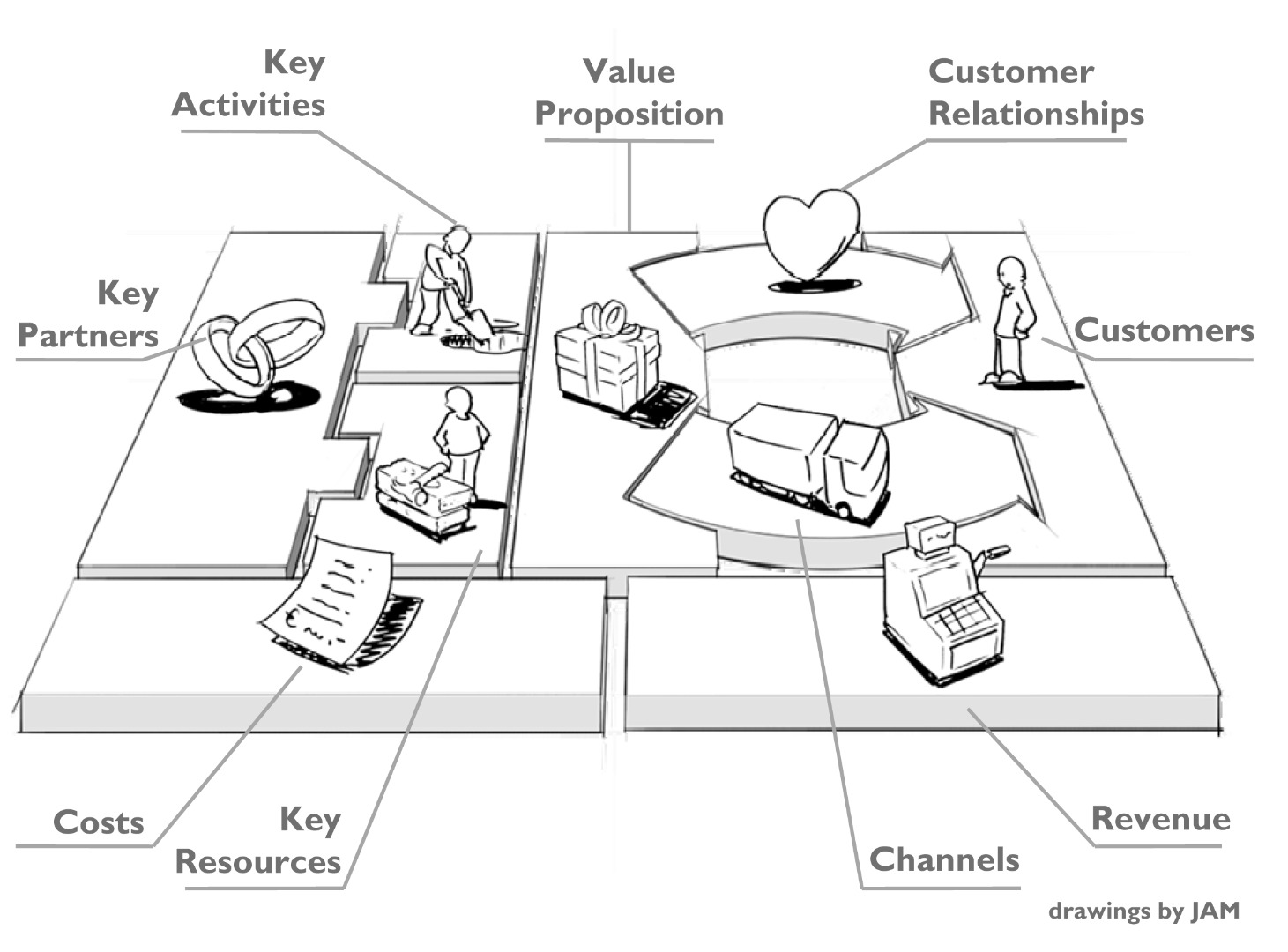
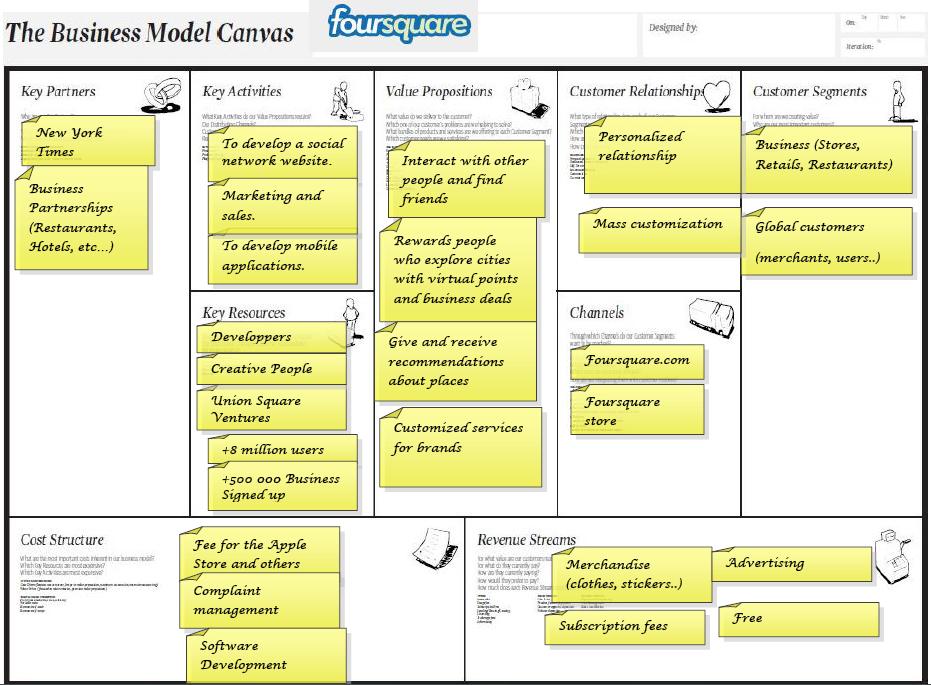
If you have a business idea, new venture, or established organization, this instructable will show you how to describe your business model on one page. A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers and captures value. The business model canvas will allow you to effectively share your business model with employees, investors, or partners. When an organization doesn't understand their business model, they experience a major breakdown in communication and goal making. Here are some companies that currently use their own Business Model Canvas: Microsoft, MasterCard, 3M, Adobe, Intel, and even NASA! When looking to understand your business model, the canvas is much better than a full business plan because it saves time and is more cooperative.
This instructable requires the designer(s) to understand all aspects of their idea or organization. This knowledge must at least be accessible and usable. Basic general business knowledge is recommended.
In addition, basic organization, communication, and teamwork skills are required to effectively make the business model canvas.
Here are the items you must gather:
1. Business Model Canvas template
Follow link: http://businessmodelgeneration.com/canvas/bmc?_ga=...
2. Appropriate writing utensil
3. Stack of Post-it Notes (at least 30)
4. (Optional) Whiteboard
5. (Optional) Business Model Generation (the book)
Follow link: http://www.amazon.com/Business-Model-Generation-Vi...
Attention: Time duration for creating a first draft Business Model Canvas usually takes from an hour to a couple days.
Tip: The Business Model Canvas creation works best when printed out on a large surface or drawn on a white board so groups of people can jointly start sketching and discussing business model elements with Post-it notes or markers.
Customer Segments

1. Reflect on your own Business
Who are you creating value for?
The first step is to find out what type of customers your organization is targeting. Below are the 5 types of customer segments. Select which one(s) apply to your organization and reflect how.
Mass Market
One large group of customers with broadly similar needs and problems. An example would be customers who need shoes.
Niche Market
One group of customers with specific needs and problems. An example would be customers who need children's shoes.
Segmented
Multiple groups of customers with slightly different needs and problems. An example would be college students attending a university.
Diversified
Multiple unrelated groups of customer segments with very different needs and problems. An example of this use would be Amazon utilizing online shoppers with Amazon.com and web developers with selling cloud computing services.
Multi-Sided Platform
Multiple independent groups of customer segments that may have different needs and problems, but the business model requires both. An example would be a credit card company that needs credit card holders and merchants who accept those credit cards.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a customer segment for your business on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Customer Segments' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many customer segments your business appeals to.
Tip: If you have multiple value propositions, use different colors of Post-it notes for their respective customer segments.
Value Propositions

1. Reflect on your own Business
What value do we deliver to the customer?
Once you know who you are providing to, then you can appeal to them with a value proposition. This part goes further than just stating your product/service, by expressing why your product/service is valuable. Below are 11 elements that contribute to customer value creation. Select which one(s) pertain to your value proposition and reflect how:
Newness
Fulfills an entirely new set of needs that customers previously didn't perceive because there was no similar value proposition.
Performance
Improves product or service performance.
Customization
Tailored to the specific needs of individual customers.
Getting the job done
Helps customers get a certain job done.
Design
Stands out because of superior design.
Brand/Status
Stands our because of the popularity or respect of a brand/status.
Price
Offers a similar value but at a lower price.
Cost Reduction
Helps customers reduce their own personal costs they would take on without the product/service.
Risk Reduction
Offer customers a chance to reduce their own risks. (Ex. 1-year guarantee)
Accessibility
Provides to customers that previously lacked access to product/service.
Convenience/Usability
Provides customers an easier way to use a vital product/service. (Ex. iTunes)
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a value proposition for your business on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Value Proposition' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many value propositions your business provides.
Channels

1. Reflect on your own Business
How do you our Customer Segments want to be reached?
These channels include communication, distribution and sales. Below are 5 channel types, select which one(s) best reflect your organization's structure and how:
Sales Force
In-person sales.
Web Sales
Online sales.
Own Stores
In-store sales.
Partner Stores
In-partner-store sales.
Wholesaler
Distributed sales.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a channel for your business on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Channels' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many channels your business utilizes.
Customer Relationships
1. Reflect on your own Business
What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to establish and maintain with them?
Connecting with your customer base is important in keeping your reputation as a caring organization. Below are 6 types of relationships to have with customers. Select which one(s) pertain to your organization and reflect how:
Personal Assistance
Customers can talk with human assistance.
Dedicated Personal Assistance
Customer representatives are directly and solely connected to an individual customer.
Self-Service
Customers are given resources to help themselves. (Ex. FAQs)
Automated Services
Customers are given customized help usually through software and automation.
Communities
Customers are able to connect with other customers for help. (Ex. Forums)
Co-Creation
Customers are able to create value for the company. (Ex. YouTube video uploads)
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a type of customer relationship your business utilizes on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Customer Relationships' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many customer relationships your business appeals to.
Revenue Streams
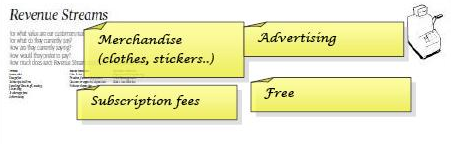
1. Reflect on your own Business
How do your Customer Segments purchase your Value Proposition?
In this step, we will find out how exactly your customers buy your product/service. Below are 6 common types of Revenue Streams. Select which one(s) pertain to your organization and reflect how:
Asset Sale
One time sale of ownership rights of a physical product.
Usage Fee
Ongoing costs to continue use of product/service. (Ex. Pay-Per-View)
Subscription Fees
Cost allowing customers to use product/service for specific time period.
Lending/Renting/Leasing
Temporarily granting someone the exclusive right to use a product/service for a specific time period.
Licensing
Granting customers permission to use protected intellectual property.
Advertising
Income through fees for advertising a particular product/service/brand.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a revenue stream your business uses on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the Revenue Streams section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many revenue streams your business utilizes.
Key Resources

1. Reflect on your own Business
What Key Resources does our business require?
This section describes the most important assets required to make a business model work. Below are 4 types of resources. For each of the 4, think of an example of what your organization uses:
Physical
Facilities, buildings, vehicles, machines, distribution networks, ect.
Intellectual
Brands, proprietary knowledge, patents, copyrights, partnerships, customer databases, ect.
Human
Key people involved in business activities.
Financial
Capital, financial guarantees, lines of credit, ect.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a key resource your business uses on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the Key Resource section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many key resources your business requires.
Key Activities
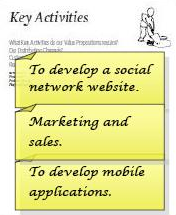
1. Reflect on your own Business
What does your business do with your resources?
In this step, we will discover the most important actions a company must take to operate successfully. Below are 3 ways activities can be categorized, think of an example of how each of them connect to your business:
Production
Relate to designing, making, and delivering a product.
Problem Solving
Relate to creating solutions to ongoing customer problems.
Platform/Network
Relate to continually maintaining Key Resources.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a key activity your business performs on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Key Activities' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many key activities your business performs.
Key Partnerships
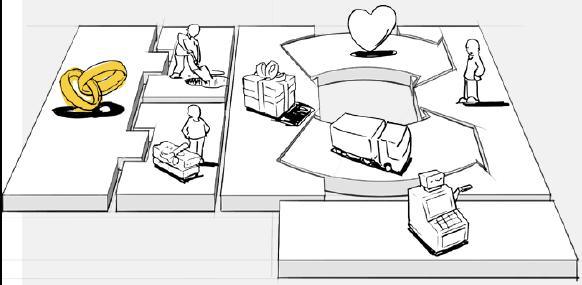

1. Reflect on your own Business
Who are your suppliers and service providers?
In this section, we will discover what partnerships your business has forged. Below are 4 types of partnerships, select which one(s) pertain to your company and how:
Strategic Alliances
Partnership between non-competitors.
Coopetition
Partnership between competitors.
Joint Ventures
Partnership between ventures to develop new a business
Buyer-Supplier
Partnership between buyers and suppliers to assure reliable supplies.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a key partnership your business has on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Key Partnership' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many key partnerships your business appeals to.
Cost Structure
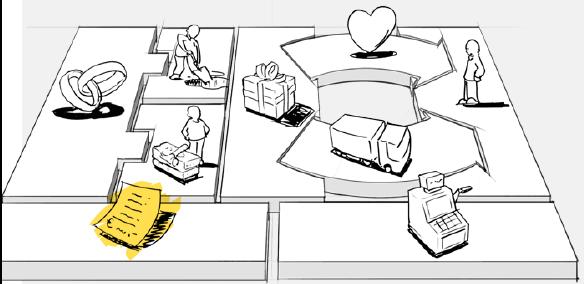

1. Reflect on your own Business
What are your most important costs?
In this step, we will develop how your company views costs and what costs it requires to operate. Below are two types of cost structures, reflect how your company chooses to utilize them:
Value-Driven
Focus on improving high value propositions.
Cost-Driven
Focus on reducing costs whenever possible.
(Attention: many business models fall in between these two structures)
Below are 4 characteristics of cost structures, reflect on how each of them may pertain to your company's costs:
Fixed Costs
Costs that remain the same no matter the volume of goods or services produced.
Variable Costs
Costs that change proportionally to the volume of goods and services produced.
Economies of Scale
Costs are reduced with the increase of the volume of goods and services produced.
Economies of Scope
Costs are reduced with the increase of business operations.
2. Fill in your Canvas
Grab a Post-it Note
Write down a cost for your business on the Post-it Note. (Tip: Refer to example for further guidance)
Stick the Post-it Note on the 'Cost Structure' section of the canvas.
Repeat process for however many costs your business has.