High Efficiency Regulated Joule Thief
by Milen in Circuits > Electronics
98658 Views, 282 Favorites, 0 Comments
High Efficiency Regulated Joule Thief




Normally the Joule thief produces output voltage, which value is difficult to predict. Without load (the LED) I have measured voltages over 30 V. I wanted to create a Joule thief, which can be used to supply some small electronic devices, but having well defined and stable output voltage. There are known some solutions in which instead the LED load, a one-diode rectifier is used, and the output voltage is stabilized by the use of Zenner diode. I did not like this solution, because through the Zenner diode flows always a constant DC current, what reduces drastically the efficiency of the device and empties fast the supply battery. I was looking for other, better solution of the output voltage stabilization (limitation).
To try my solution, at first, I needed to build the standard working Joule thief. How to do this - there are a lot of articles and internet sites (for example this). How to find the needed parts? - I knew that inside the high efficiency lighting bulbs are some parts, which could be re-used. I had a defect bulb and I carefully cut the plastic box. From there I extracted the voltage converting board. On these PCB's can be found some very useful stuff : HV diodes, chokes, HV capacitors, HV transistors..etc (HV means high voltage ~ 400V). I took the ferrite toroidal transformer, cut and removed all its wires. After that I disassembled the choke. I took around one meter enamelled wire from it, and winded it around the ferrite bead. Because the wire was fold, I winded simultaneously two coils having ~ 50 turns. Having the main part of the Joule thief (the transformer) ready, the remaining work is not much.. The only tricky in the design is to connect both coils in the correct way. (see the mentioned link for additional information). So designed the Joule thief was able to produce 34 V voltage measured on the collector node of the NPN transistor (2N2222) without any load, when supplied by 1.2V AAA battery (filterd with 2.2uF capacitor).
To try my solution, at first, I needed to build the standard working Joule thief. How to do this - there are a lot of articles and internet sites (for example this). How to find the needed parts? - I knew that inside the high efficiency lighting bulbs are some parts, which could be re-used. I had a defect bulb and I carefully cut the plastic box. From there I extracted the voltage converting board. On these PCB's can be found some very useful stuff : HV diodes, chokes, HV capacitors, HV transistors..etc (HV means high voltage ~ 400V). I took the ferrite toroidal transformer, cut and removed all its wires. After that I disassembled the choke. I took around one meter enamelled wire from it, and winded it around the ferrite bead. Because the wire was fold, I winded simultaneously two coils having ~ 50 turns. Having the main part of the Joule thief (the transformer) ready, the remaining work is not much.. The only tricky in the design is to connect both coils in the correct way. (see the mentioned link for additional information). So designed the Joule thief was able to produce 34 V voltage measured on the collector node of the NPN transistor (2N2222) without any load, when supplied by 1.2V AAA battery (filterd with 2.2uF capacitor).
The Regulating Circuit


After finishing the original Joule thief, I have created the additional circuit, which controls the output voltage. It is based on the use of bipolar transistor Schmitt trigger. Its input is connected to the middle point of variable resistive voltage divider placed between the regulated supply voltage and the common ground node.The output of the Schmitt trigger connects to the gate of NMOS switch transistor. The drain terminal of this switch connects to the base of the Joule thief oscillator transistor. The principle of work of the control circuit is following: After start up, the supply voltage increases with the time. This voltage is produced by simple half wave Schottky diode rectifier with capacitive filter (the 3.3 uF 350V capacitor). The input voltage at the Schmitt trigger input (which is part of the supply voltage) increases also proportionally to the supply voltage and the value of the variable bottom resistor of the voltage divider. When the supply voltage reaches a programmed by the voltage divider value, the Schitt trigger switches to other state thus changing its output voltage from low to high. This closes the NMOS switch, which respectively shorts the base terminal of the oscillating transistor to ground, blocking in this way the further oscillations. When the oscillations stop, the increasing of the supply voltage also stops. The energy storing (filtering) capacitor discharges slowly through the load. The output voltage starts to decrease. This process continues until the "high to low" threshold of the Schmitt trigger is reached. Then it changes again its state and the NMOS switch opens. The oscillations start again the supply voltage starts to increase again...until the threshold voltage "low to high" of the Schmitt triggers is reached...and this sequence can continue until the supply battery is empty. The supply voltage is kept in range which can be narrow (depends on the Schmitt trigger hysteresis and ratio of the used resistors in the voltage divider). Because two phases of regulation exist - active (when the oscillator works) and passive (when the needed current for the load is delivered only by the energy storing capacitor), the efficiency of the regulated Joule thief is high - it consumes energy from the supply battery only during the first phase.
To help you better to understand the principle of work of the device, I have attached its schematic file which can be simulated by the Linear LTspice circuit simulator. Its is easy to use, free Spice simulator, which can be used for electrical simulation of different analog and digital circuits. You can download it from here. The circuit is ready for simulation, without any additional changes. You can look at the transient voltages and currents in the schematic, to change the values of the devices...and to play a lot...
On the pictures I have presented the circuit and some voltage transients signals.
To help you better to understand the principle of work of the device, I have attached its schematic file which can be simulated by the Linear LTspice circuit simulator. Its is easy to use, free Spice simulator, which can be used for electrical simulation of different analog and digital circuits. You can download it from here. The circuit is ready for simulation, without any additional changes. You can look at the transient voltages and currents in the schematic, to change the values of the devices...and to play a lot...
On the pictures I have presented the circuit and some voltage transients signals.
Downloads

The list of the used parts:
- 1x ferrite bead
- 1m copper wire
- a piece of veroboard
- 3 x 2N2222 NPN transistor - can be other NPN BJT with Beta>50
- 1 x 2.2uF(3.3uF) 400V capacitor
- 1 x 240 KOhm resistor
- 1 x 200 KOhm resistor (150-250 is OK)
- 1 x 57 KOhm resistor
- 1 x 10 Ohm (10-100) resistor
- 1 x 30KOhm potentiometer
- 1 x BSS123 NMOS transistor (other NMOS fast switching transistor should be OK)
- 1 x Schottky diode ( for 200mA, 40V...small signal should be OK)

Common feature of the Joule thief, supplied by a 1.5V single battery, is that is not able to deliver much of energy. It can be used to supply a LED diode/s , some low consumption electronic device...etc. It is possible to complicate the circuit, adding 3-rd coil, which can have more turns and can produce higher voltage.
My regulated Joule thief I supply with one AAA battery. It is able to work with battery, which is ~ 0.35 V. The output voltage can vary from 1.5 to 16V. If a supply source, which must work with low supply voltages, but must not deliver big currents, is needed - the proposed circuit is ideal solution. If the supply noise (oscillations around one value) is not desired, additional LP (low pass) filter or LDO regulator can be placed. The output voltage of the regulated Joule thief can be adjusted so, that it is enough high, to allow the LDO to work in the proper regime. In this way over the pass transistor of the LDO the voltage drop should small and the energy efficiency shall be kept again high.
To estimate the power driving capabilities of the proposed circuit, I did the following experiment:
I have loaded the circuit with a potentiometer. I have adjusted the output voltage to be 5V when the load resistance is 10 KOhm (0.5mA current), and measuring both the output voltage, and the flowing through the resistor current for different load resistance values, I made the following graph. There can be seen that the circuit deliver up to 3mA current at relatively stable output voltage, and further the output voltage drops down. Of course this curve is valid only for my particular implementation, and can differ a lot for different one, but it shows a common behavior, which this circuit implementation will have. The bend point ( in my case ~ 3 mA ) is the moment, where the whole energy inserted in the storage capacitor is delivered as power in the load, and the toggling of the Schmitt trigger stops.
My regulated Joule thief I supply with one AAA battery. It is able to work with battery, which is ~ 0.35 V. The output voltage can vary from 1.5 to 16V. If a supply source, which must work with low supply voltages, but must not deliver big currents, is needed - the proposed circuit is ideal solution. If the supply noise (oscillations around one value) is not desired, additional LP (low pass) filter or LDO regulator can be placed. The output voltage of the regulated Joule thief can be adjusted so, that it is enough high, to allow the LDO to work in the proper regime. In this way over the pass transistor of the LDO the voltage drop should small and the energy efficiency shall be kept again high.
To estimate the power driving capabilities of the proposed circuit, I did the following experiment:
I have loaded the circuit with a potentiometer. I have adjusted the output voltage to be 5V when the load resistance is 10 KOhm (0.5mA current), and measuring both the output voltage, and the flowing through the resistor current for different load resistance values, I made the following graph. There can be seen that the circuit deliver up to 3mA current at relatively stable output voltage, and further the output voltage drops down. Of course this curve is valid only for my particular implementation, and can differ a lot for different one, but it shows a common behavior, which this circuit implementation will have. The bend point ( in my case ~ 3 mA ) is the moment, where the whole energy inserted in the storage capacitor is delivered as power in the load, and the toggling of the Schmitt trigger stops.




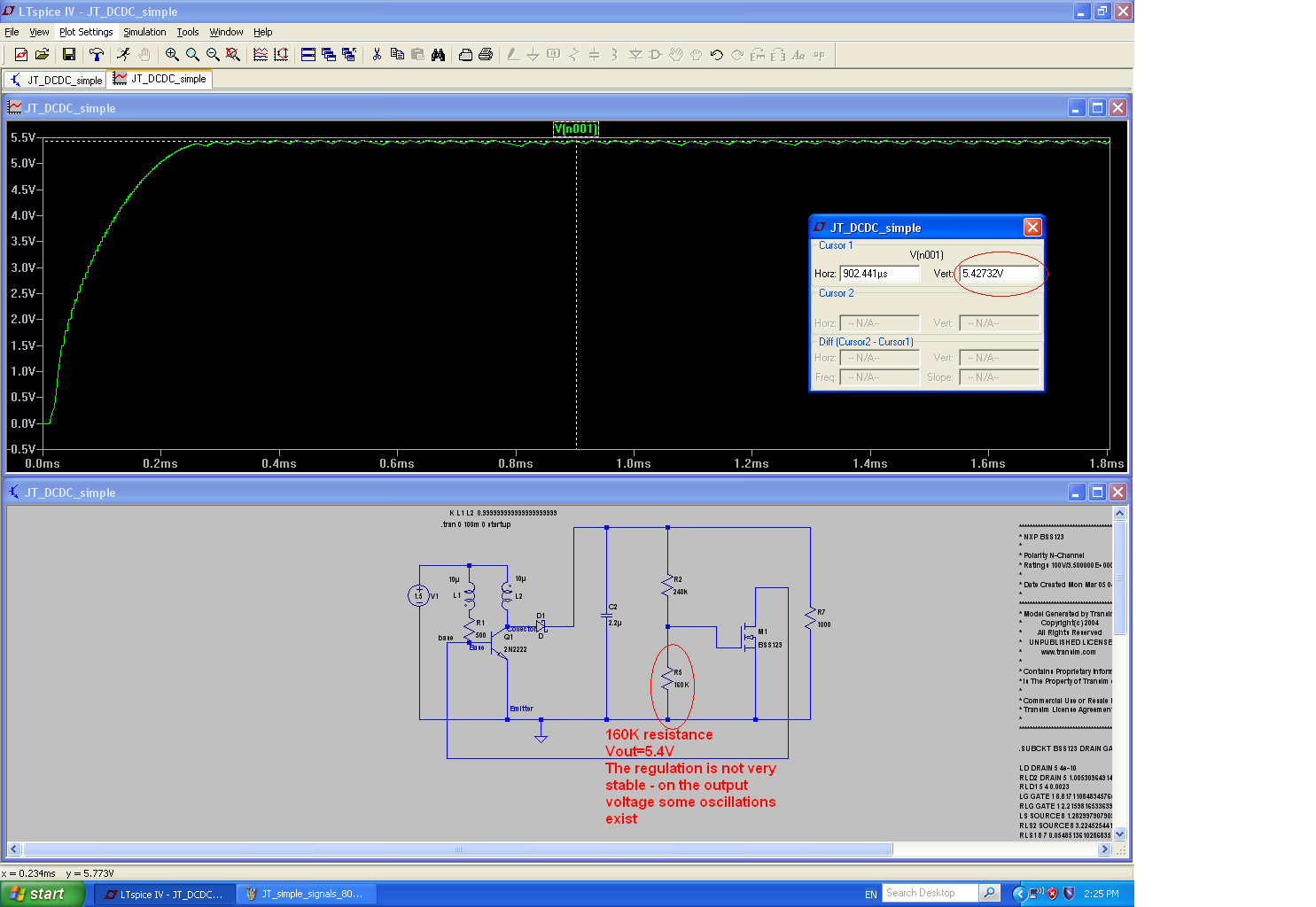
After some discussions I decided to try to simplify the circuit. I found the following solution - simply removed the Schmitt trigger and connected the gate of the NMOS switch directly to the middle point of the resistive voltage divider. As mentioned before, this divider can be replaced by a single potentiometer ( 270 KOhm). With its help the division ratio can be changed, thus adjusting the output voltage. The voltage at the gate of the NMOS switch stays close the the Vth (threshold voltage) of the NMOS switch. The new schematic and some simulations results can be seen on the pictures. There can be seen that for some resistor values, the low frequency oscillation, which was caused by the Schmitt trigger transitions around its threshold voltages disappear. The output voltage is more smooth. May be with the time it will drift more than the voltage generated by the previous version (with the Schmitt trigger). For some resistor values, in the simpler implementation, can be seen also low frequency oscillation, which amplitude is not so stable, as the Schmitt trigger version.
There is a way to increase the efficiency of the Schmitt trigger version. It can be used when higher power will be needed, what means that the base resistor will be relatively small and the DC current flowing from the supply to the ground node through this resistor and the NMOS switch during the non-active phase could be high. The solution is to break the path of the current by the use of additional PMOS switch placed in series with the base resistor, with source connected to the supply, drain connected to top terminal of inductance L1, and gate connected to the output of the Schmitt trigger. Thus: When the base of the BJT is grounded by the NMOS switch, the PMOS switch will be open and no DC current will pas through. When the output of the Schmitt trigger has low logical state the PMOS will be closed and will connect the bottom terminal of the inductance L1 to the supply source, what corresponds to the active phase of work. To be able to use small supply voltages (<1.5V) in this case the PMOS switch must he chosen so, that it has low Ron (switch "ON" resistance) and low Vth ( threshold voltage). Normally the DMOS devices satisfy these requirements. Could be used also JFET transistor. In this case the base resistor could be even omitted.
As conclusion - both versions can be used for applications, where the supply noise is not important. The output voltage can be set to some defined value by the use of the potentiometer and will have some oscillations around this operational point. Because the oscillation frequency is relatively high (more than 50 KHz), the regulated JT could be used also for supplying even of audio devices. If better noise performance is needed, then filtering of the output voltage should be implemented.
There is a way to increase the efficiency of the Schmitt trigger version. It can be used when higher power will be needed, what means that the base resistor will be relatively small and the DC current flowing from the supply to the ground node through this resistor and the NMOS switch during the non-active phase could be high. The solution is to break the path of the current by the use of additional PMOS switch placed in series with the base resistor, with source connected to the supply, drain connected to top terminal of inductance L1, and gate connected to the output of the Schmitt trigger. Thus: When the base of the BJT is grounded by the NMOS switch, the PMOS switch will be open and no DC current will pas through. When the output of the Schmitt trigger has low logical state the PMOS will be closed and will connect the bottom terminal of the inductance L1 to the supply source, what corresponds to the active phase of work. To be able to use small supply voltages (<1.5V) in this case the PMOS switch must he chosen so, that it has low Ron (switch "ON" resistance) and low Vth ( threshold voltage). Normally the DMOS devices satisfy these requirements. Could be used also JFET transistor. In this case the base resistor could be even omitted.
As conclusion - both versions can be used for applications, where the supply noise is not important. The output voltage can be set to some defined value by the use of the potentiometer and will have some oscillations around this operational point. Because the oscillation frequency is relatively high (more than 50 KHz), the regulated JT could be used also for supplying even of audio devices. If better noise performance is needed, then filtering of the output voltage should be implemented.