Data Logger
.png)
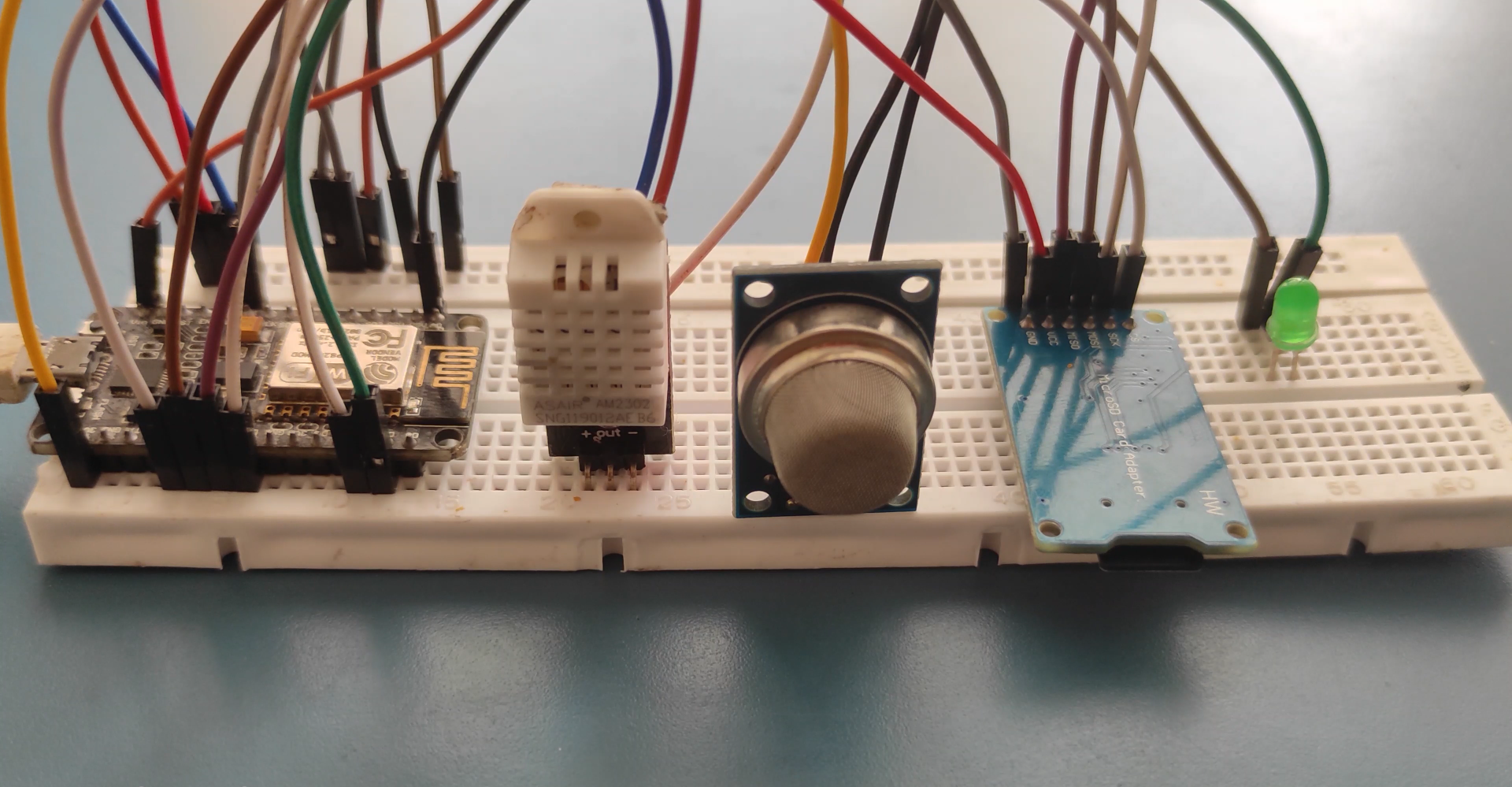
This is a simple data logger to save sensor values to sd card for future use
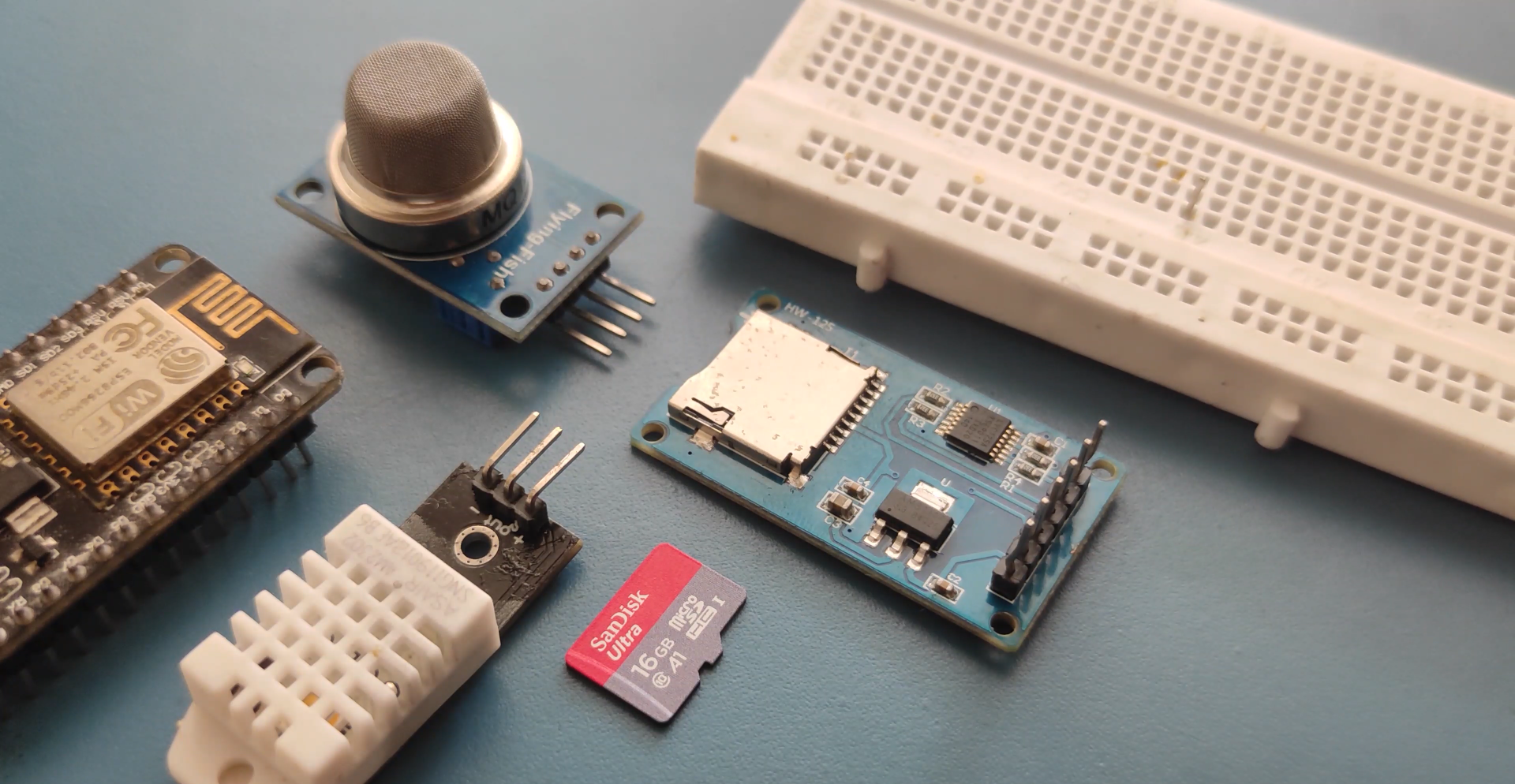
Supplies
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
If you have hard-time 3d printing stuff and other materials which i have provided in this project please refer the professionals for the help, JLCPCB is one of the best company from shenzhen china they provide, PCB manufacturing, PCBA and 3D printing services to people in need, they provide good quality products in all sectors
Please use the following link to register an account in JLCPCB
Pcb Manufacturing
----------
2 layers
4 layers
6 layers
PCBA Services
JLCPCB have 350k+ Components In-stock. You don’t have to worry about parts sourcing, this helps you to save time and hassle, also keeps your costs down.
Moreover, you can pre-order parts and hold the inventory at JLCPCB, giving you peace-of-mind that you won't run into any last minute part shortages. jlcpcb.com/RNA
3d printing
-------------------
SLA -- MJF --SLM -- FDM -- & SLS. easy order and fast shipping makes JLCPCB better companion among other manufactures try out JLCPCB 3D Printing servies
JLCPCB 3D Printing starts at $1 &Get $54 Coupons for new users
A data logger (also datalogger or data recorder) is an electronic device that records data over time or about location either with a built-in instrument or sensor or via external instruments and sensors. Increasingly, but not entirely, they are based on a digital processor (or computer), and called digital data loggers (DDL). They generally are small, battery-powered, portable, and equipped with a microprocessor, internal memory for data storage, and sensors. Some data loggers interface with a personal computer and use software to activate the data logger and view and analyze the collected data, while others have a local interface device (keypad, LCD) and can be used as a stand-alone device.
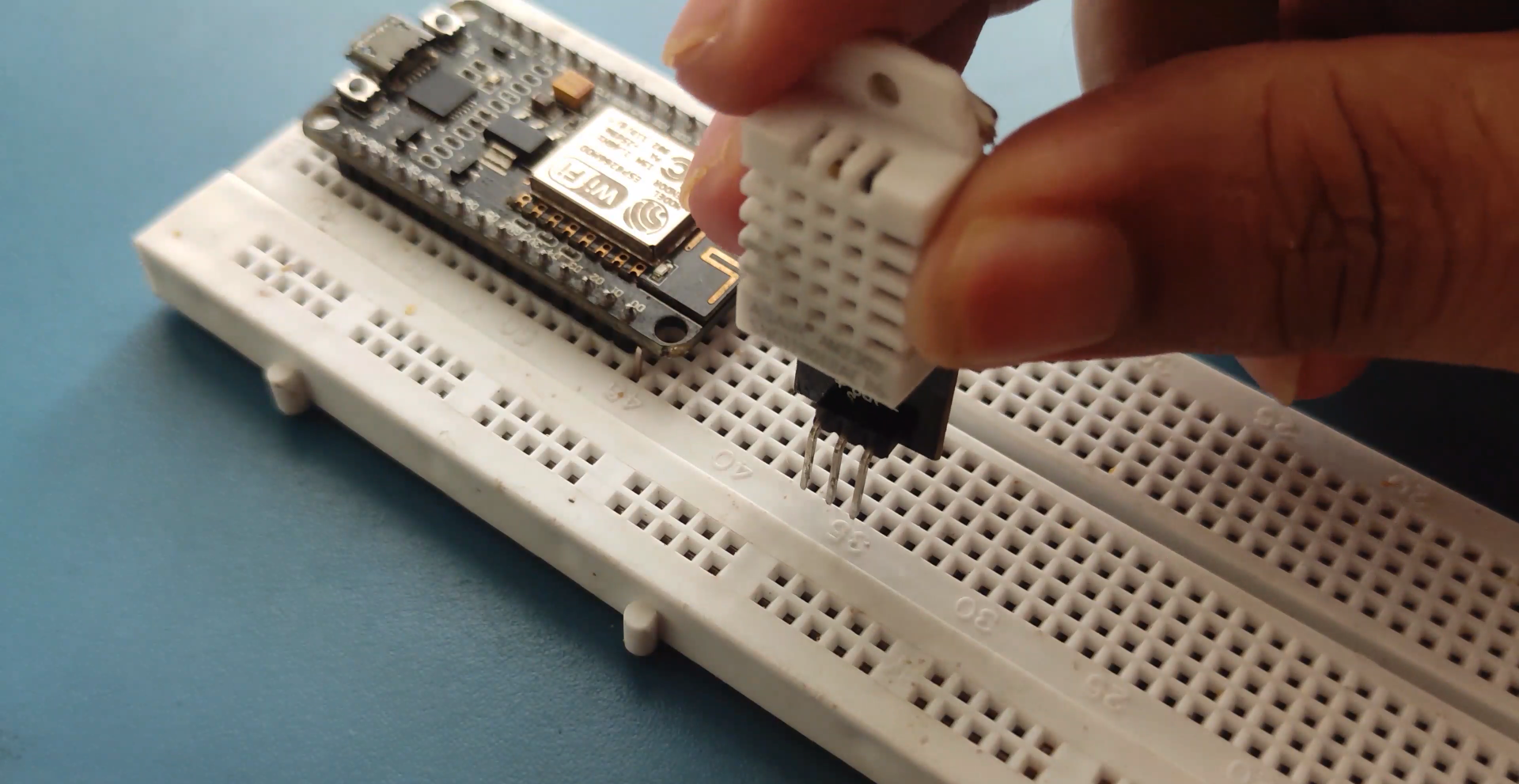
The data saved can be easily opened in an Excel Sheet for further analyses. To maintain the date and time we will use the famous RTC module DS3231 and to get the Temperature and Humidity we will use the DHT11 Sensor.
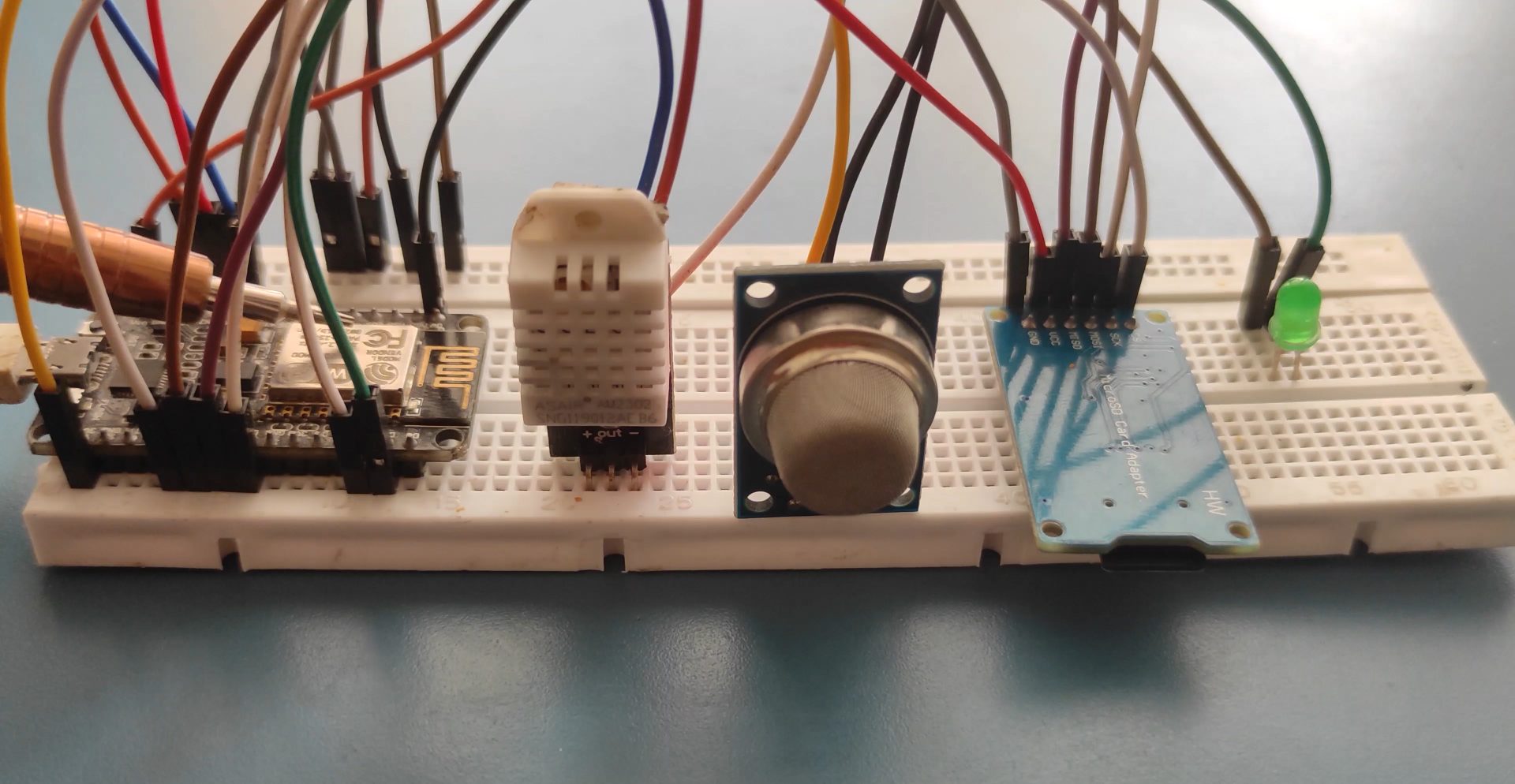
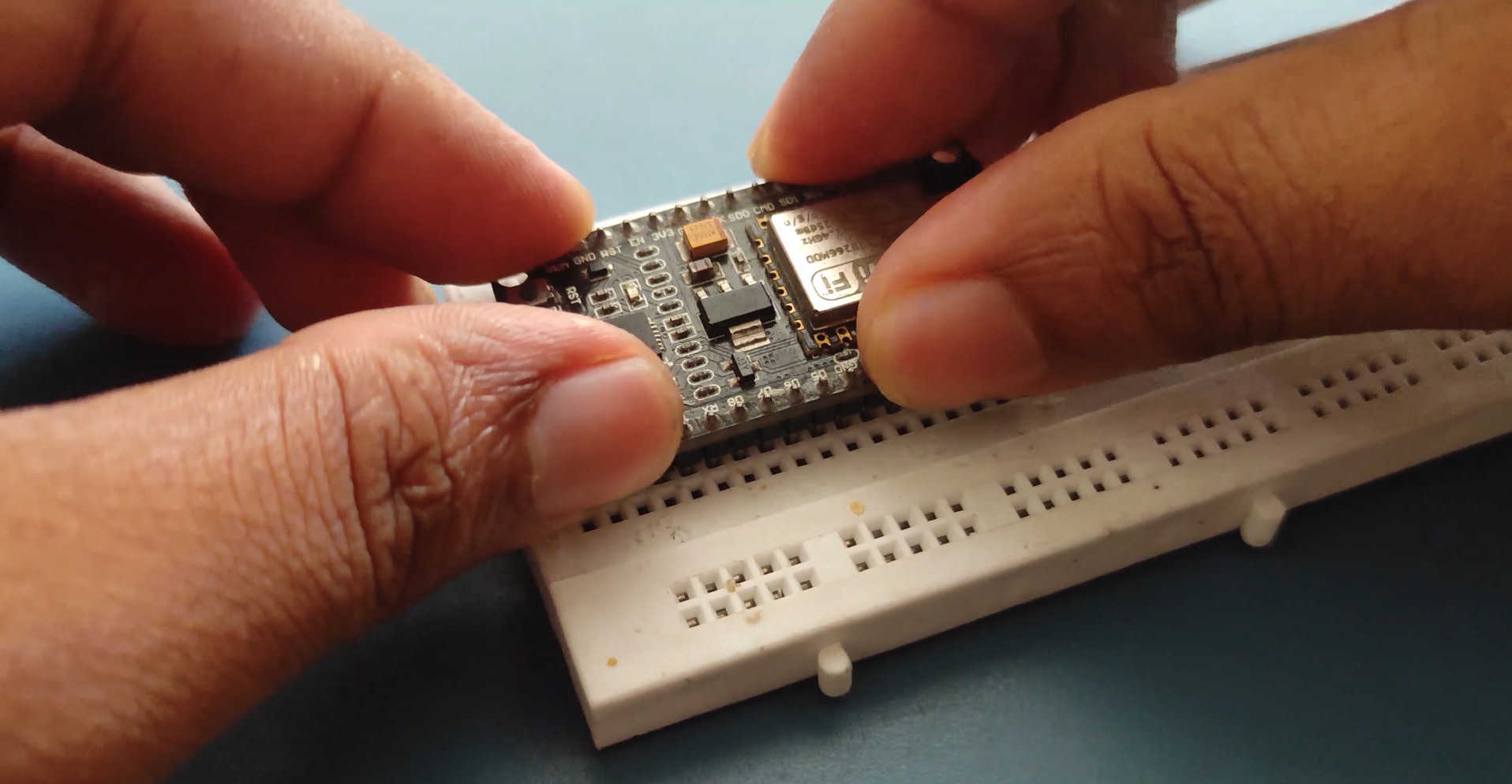
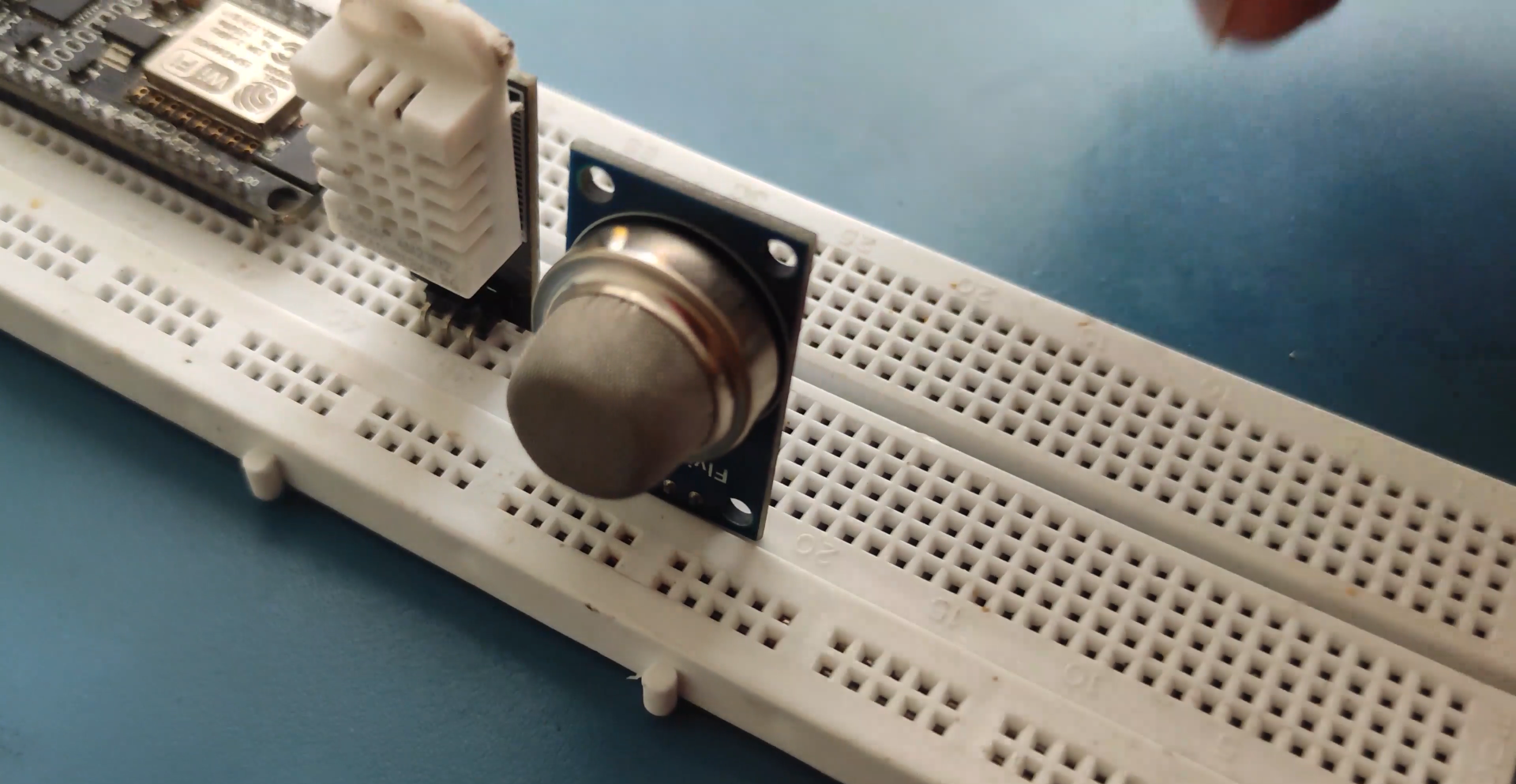
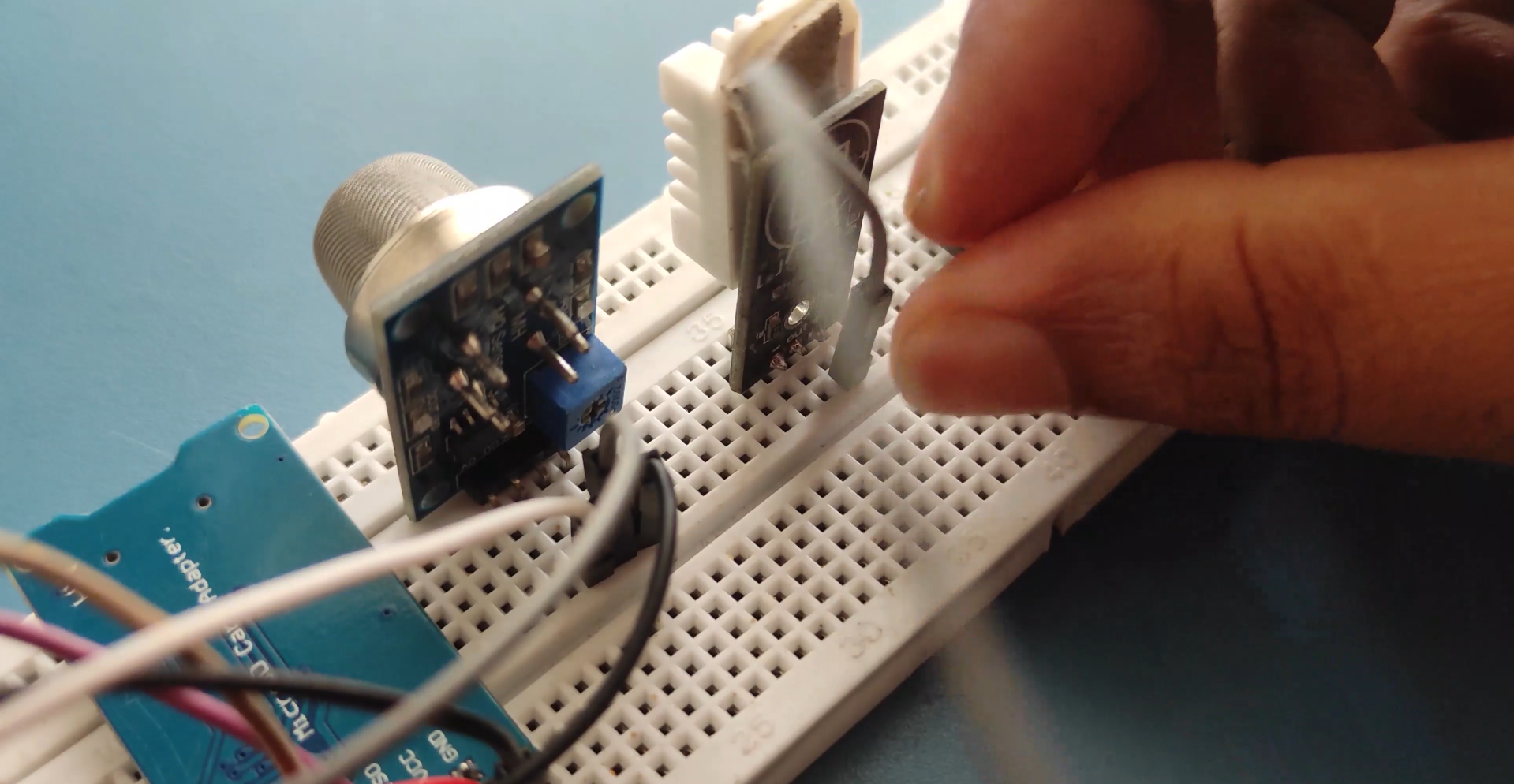
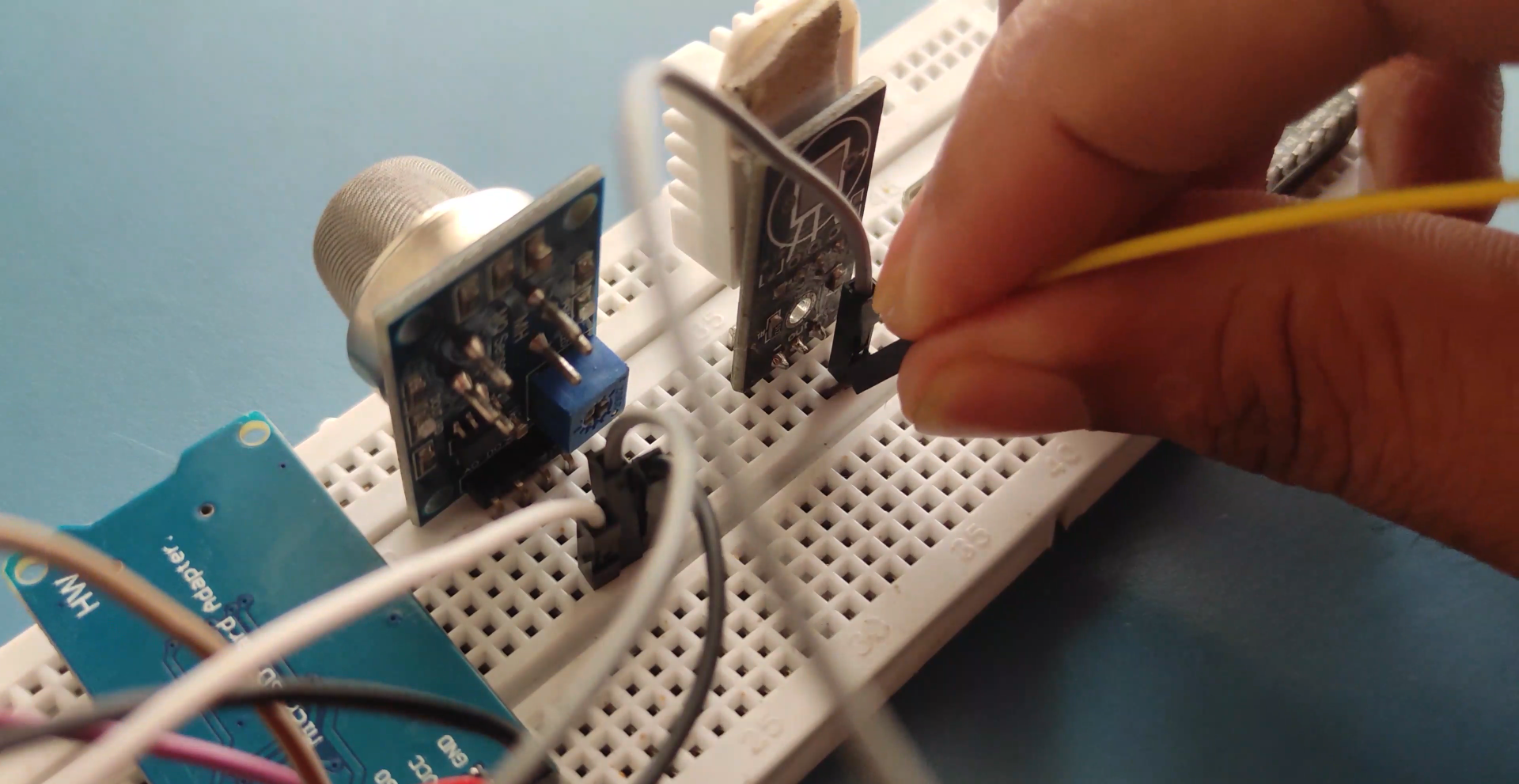
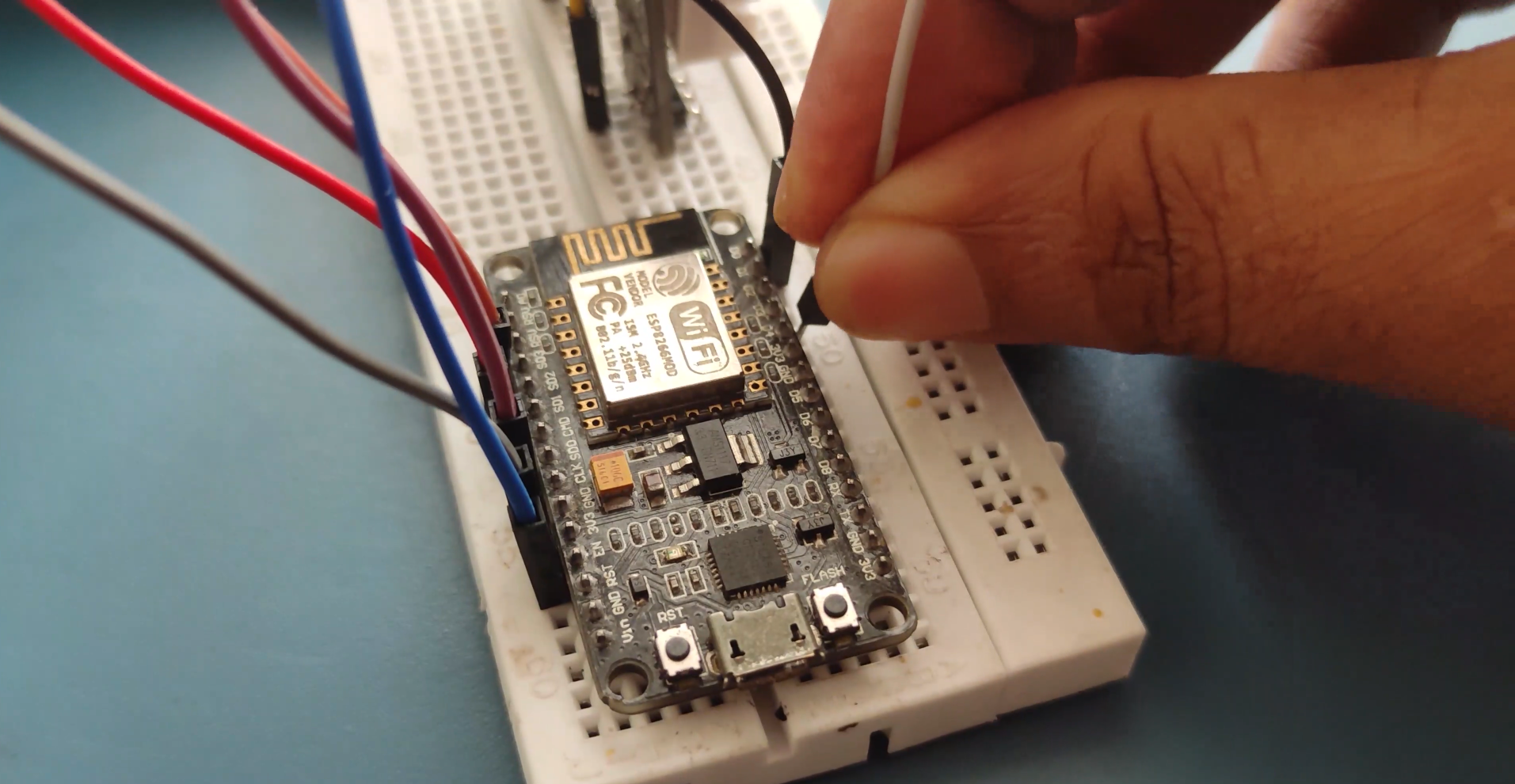
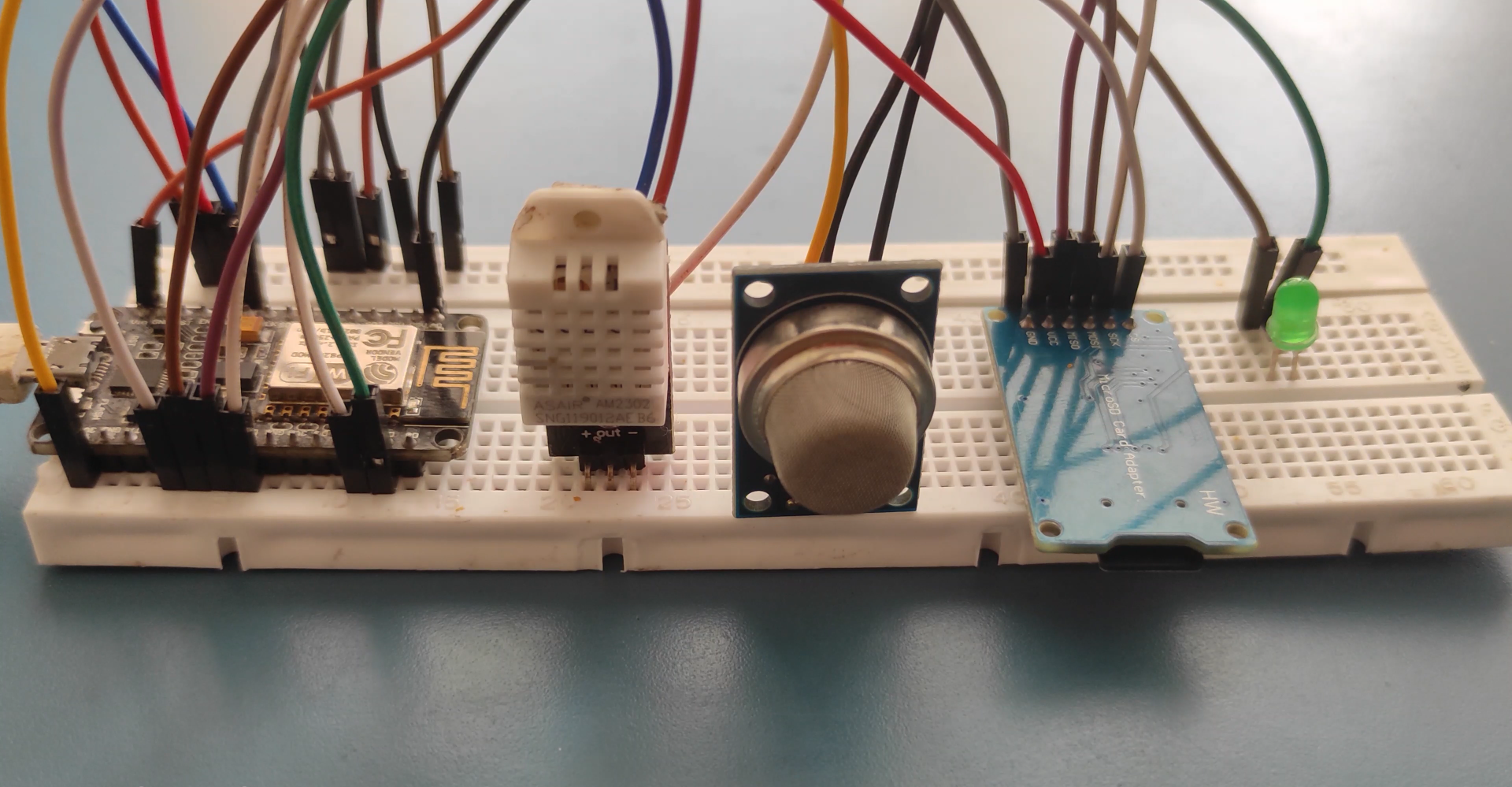
Wiring
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
We have to write the Arduino program which can do the following.
- Read data from DTH11 Sensor (or any other data that you wish to log).
- Initialize the I2C bus to read data from RTC module.
- Initialize the SPI bus to interface the SD card module with Arduino.
- Store the Date, Time, Temperature and Humidity into the SD card.
- Store the Date, Time, Temperature and Humidity on a Excel Sheet running on a computer/Laptop.
The above steps might sound complicated but they are very easy since we have the libraries to do the hard job for us. You have to download the following two libraries
To feed the data from Arduino lively into an Excel sheet on computer we will also need to install software called PLX-DAQ provided by Parallax Inc. Follow the link to download the file and install them based on your operating system. This should have created a folder named PLS-DAQ on your desktop. We will take care of it later in our working section.
1. Reading Data from DS3231:
DS3231 is a RTC (Real Time Clock) module. It is used to maintain the date and time for most of the Electronics projects. This module has its own coin cell power supply using which it maintains the date and time even when the main power is removed or the MCU has gone though a hard reset. So once we set the date and time in this module it will keep track of it always.
Using this module is very easy because of the library provided by Arduino.
// Init the DS3231 using the hardware interface
DS3231 rtc(SDA, SCL);
void Initialize_RTC()
{
// Initialize the rtc object
rtc.begin();
//#### the following lines can be uncommented to set the date and time for the first time###
/*
rtc.setDOW(FRIDAY); // Set Day-of-Week to SUNDAY
rtc.setTime(18, 46, 45); // Set the time to 12:00:00 (24hr format)
rtc.setDate(6, 30, 2017); // Set the date to January 1st, 2014
*/
}
In the loop section using the Serial.print() funtion we will print the time and the temperature values on the serial monitor, with a “comma” character between them and a new line after the temperature value. We need this form of the lines so that we can easily import them and make a chart in Excel. Also note that the temperature values are converted into integers.
So these same values will also be written into the newly created “test.txt” file and at the end we just need to add a delay which will represent the interval of recording the temperature data.
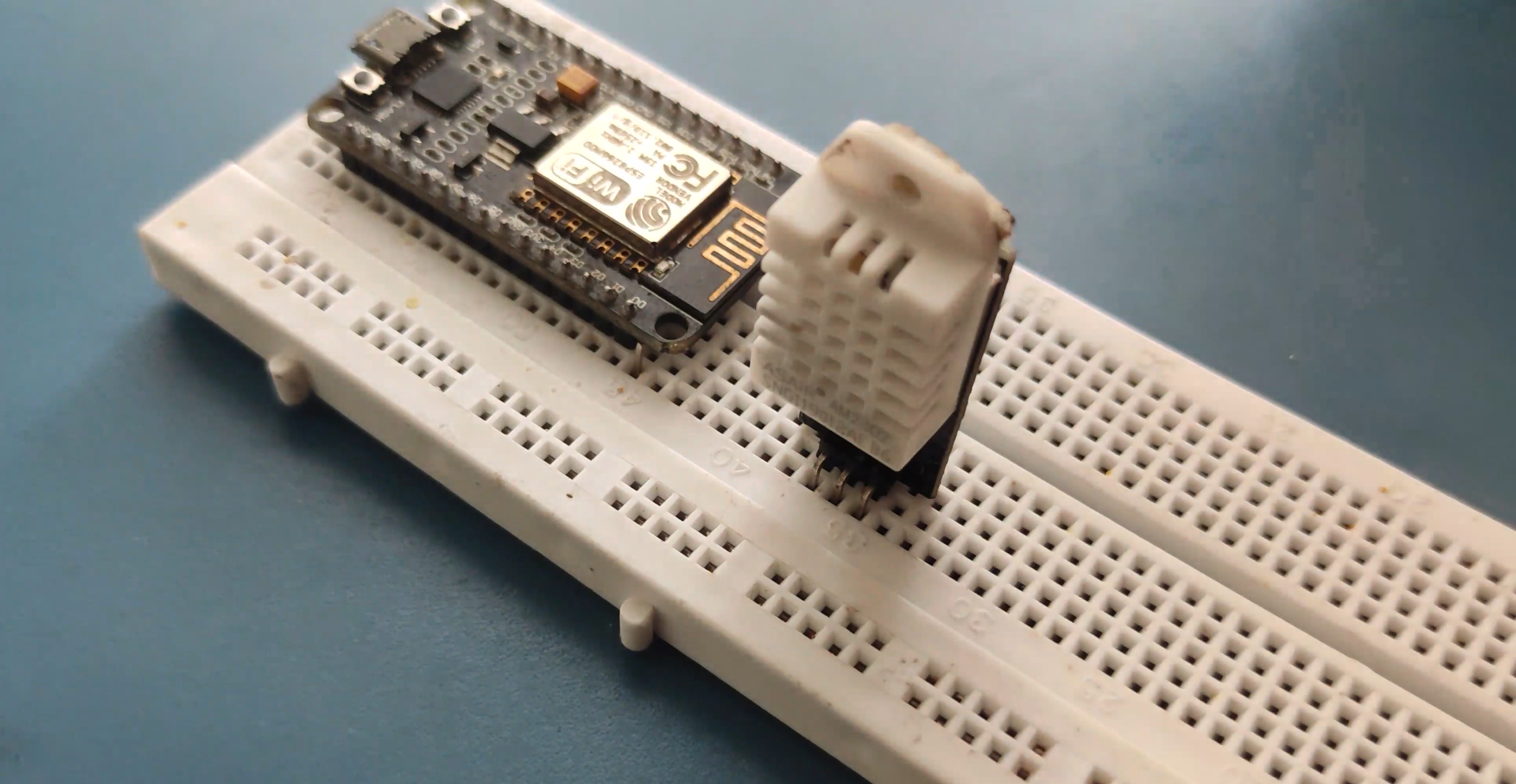
NODEMCU Wiring..
.png)
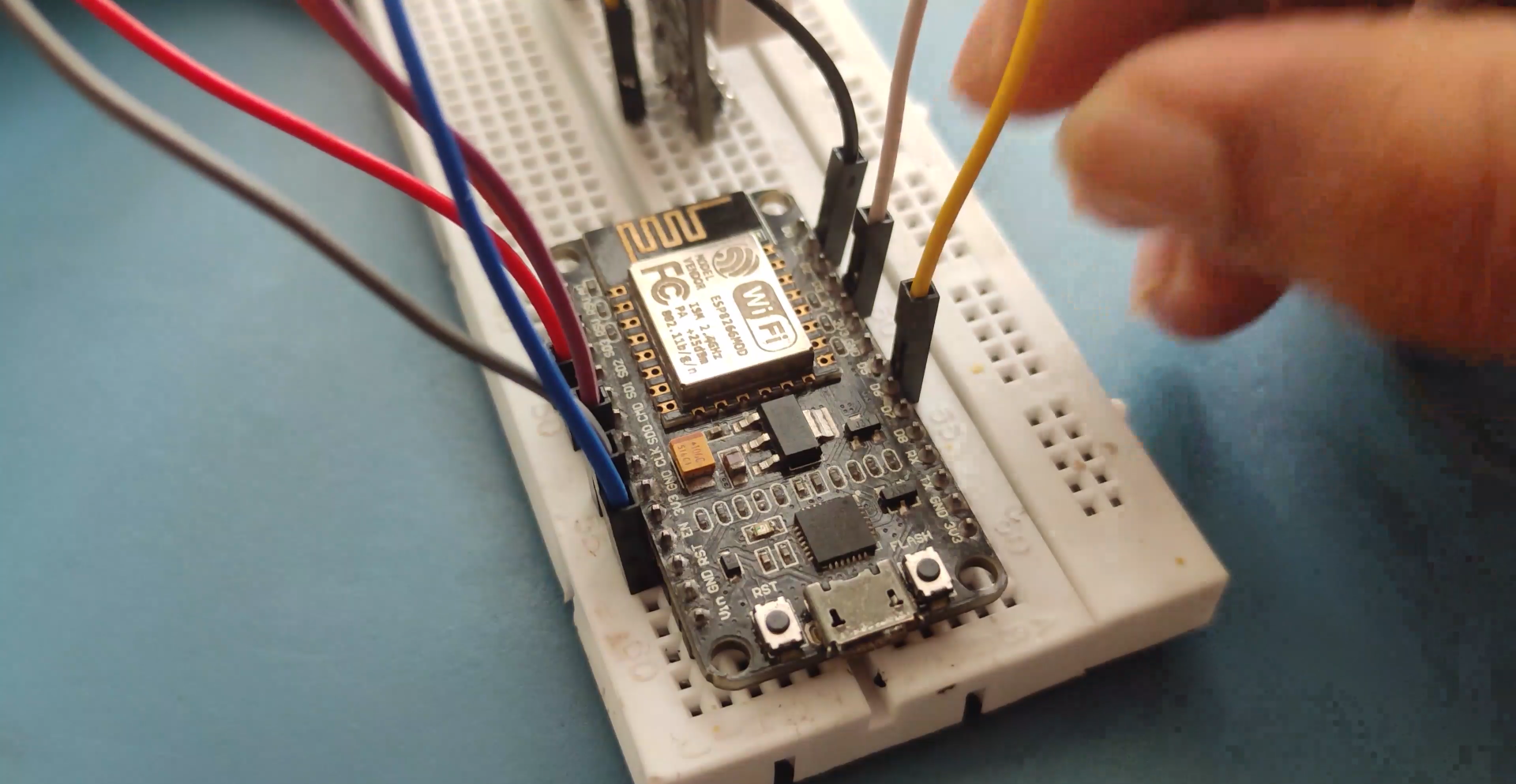.png)
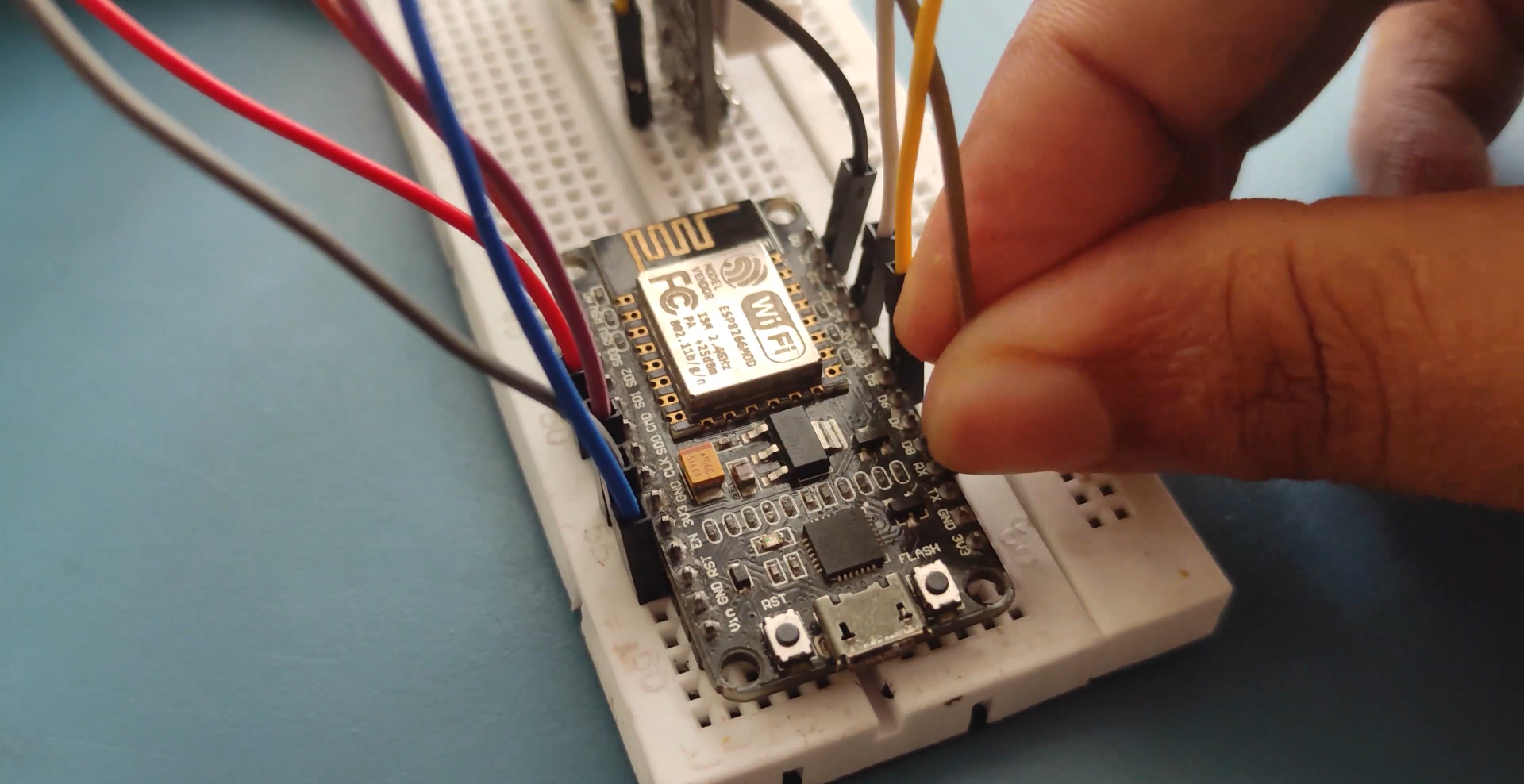.png)
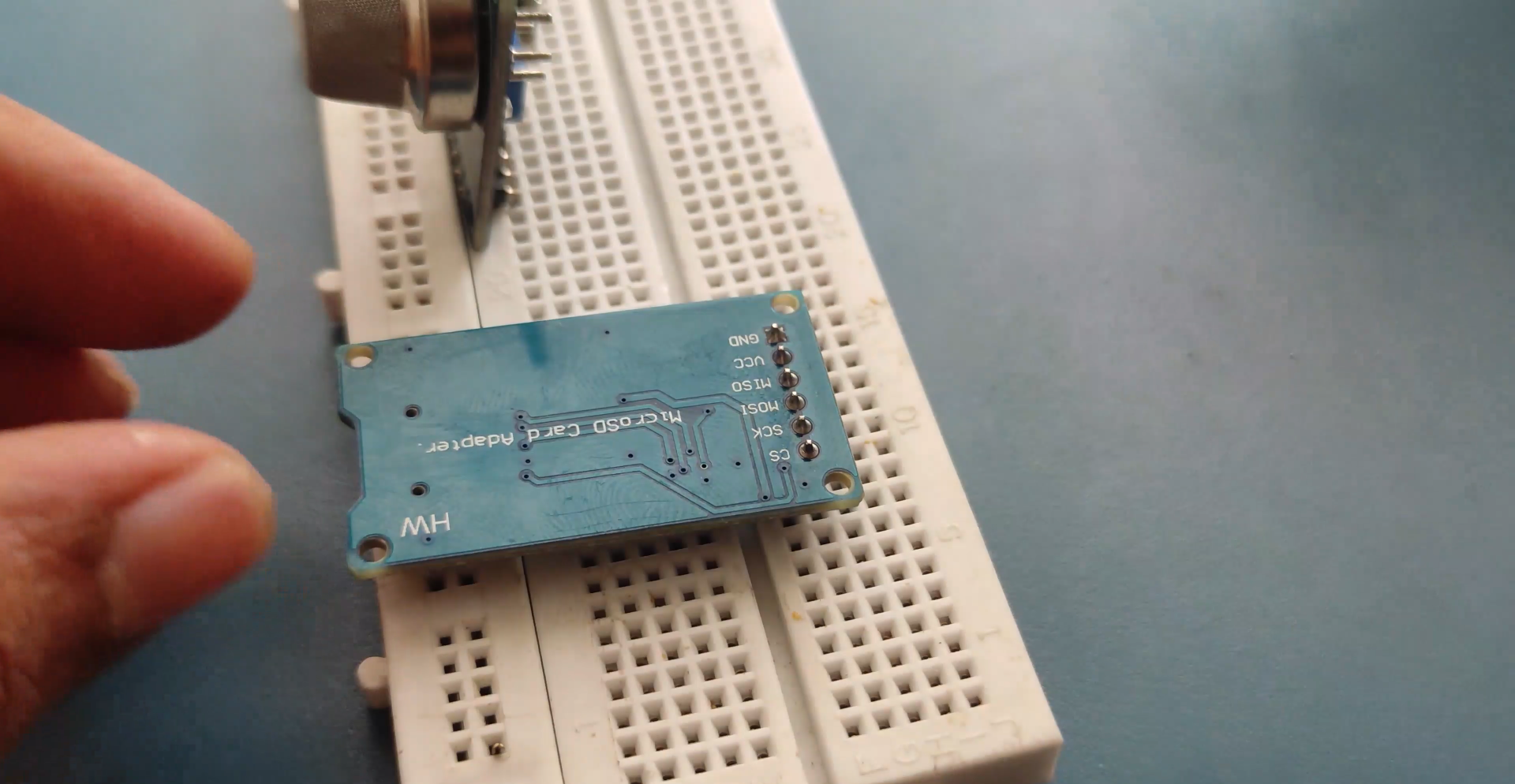
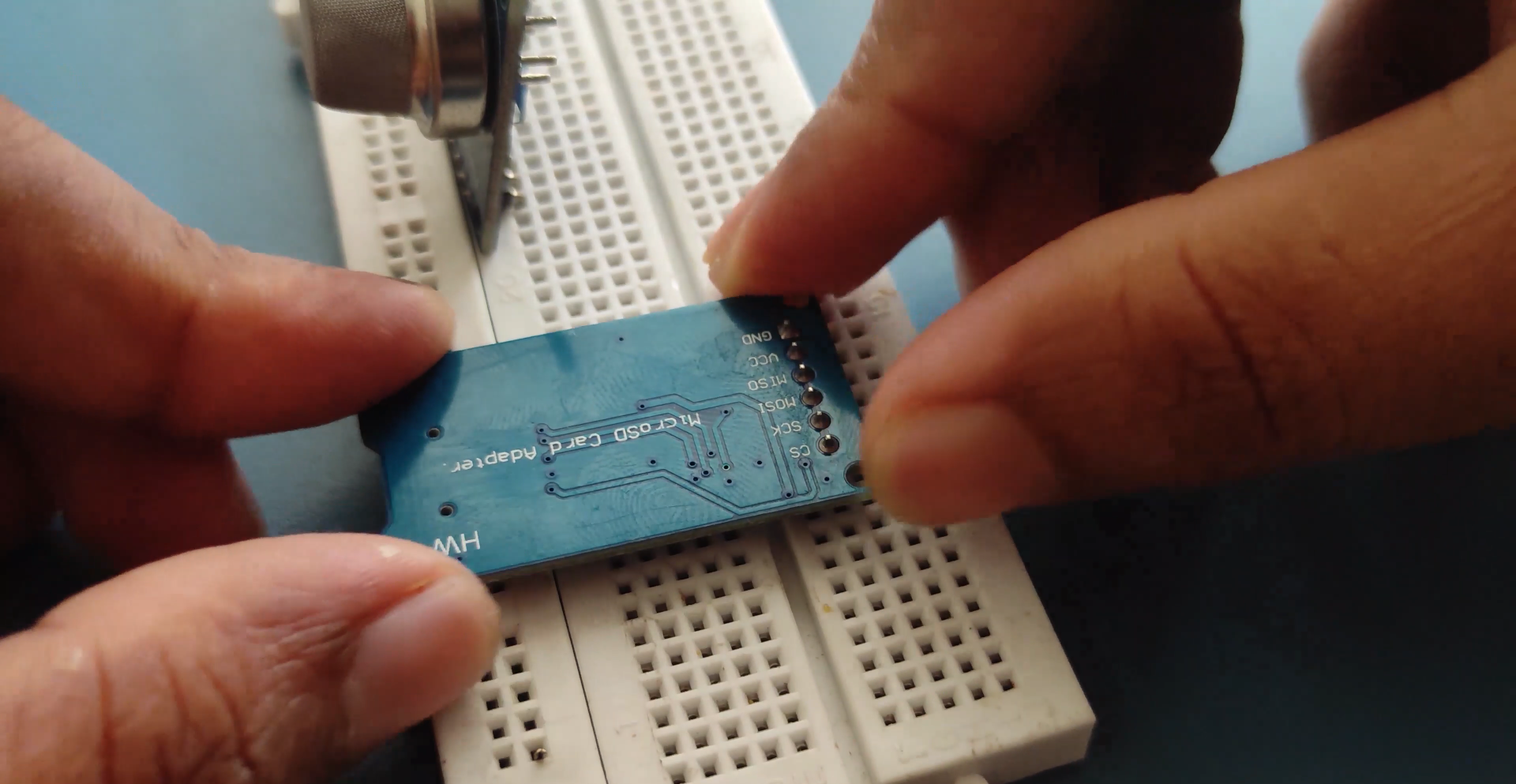
Using an SD card with Arduino is easy because of the SD card library which will be added to the Arduino IDE by default. In the SD card initialize function we will create a text file named “LoggerCD.txt” and write the first row of our content. Here we separate the values by using a “,” as a delimiter. Meaning when a comma is placed it means we have to move to the next cell in the Excel sheet.
As said earlier our intention is to save the Date, Time, Temperature and Humidity into our SD card. With the help of the DS3231 library and the DHT11 library our Arduino will be capable of reading all these four parameters
Writing Data to PLX-DAQ
PLX-DAQ is Microsoft Excel Plug-in software that helps us to write values from Arduino to directly into an Excel file on our Laptop or PC. This is my personal favourite because of two reasons:
1.You can write and monitor the data at the same time and provides us way to plot them as graphs.
2. You do not need a RTC Module like DS3231 to keep track of date and time. You can simply use the date and time running on your Laptop/computer and save them directly on Excel.
Setting the Data
.png)
.png)
if the file has been successfully created first we will print the string “Writing to file” on the serial monitor and then using the myFile.println() function we will print the text “Testing text 1, 2 ,3…” into the file. After that we need to use close() function to ensure that the previous data written to the file is physically saved to the SD Card.
Next, we will see how we can read from the file. So again we will the same function, SD.open(), but this time as the file “test.txt” has already been created, the function will just open the file. Then using the myFile.read() function we will read from the file and print it on the serial monitor. The read() function actually reads just one character at a time, so therefore we need to use the “while” loop and the function myFile.available() to read all characters or the whole previously written data. At the end we need to close the file.
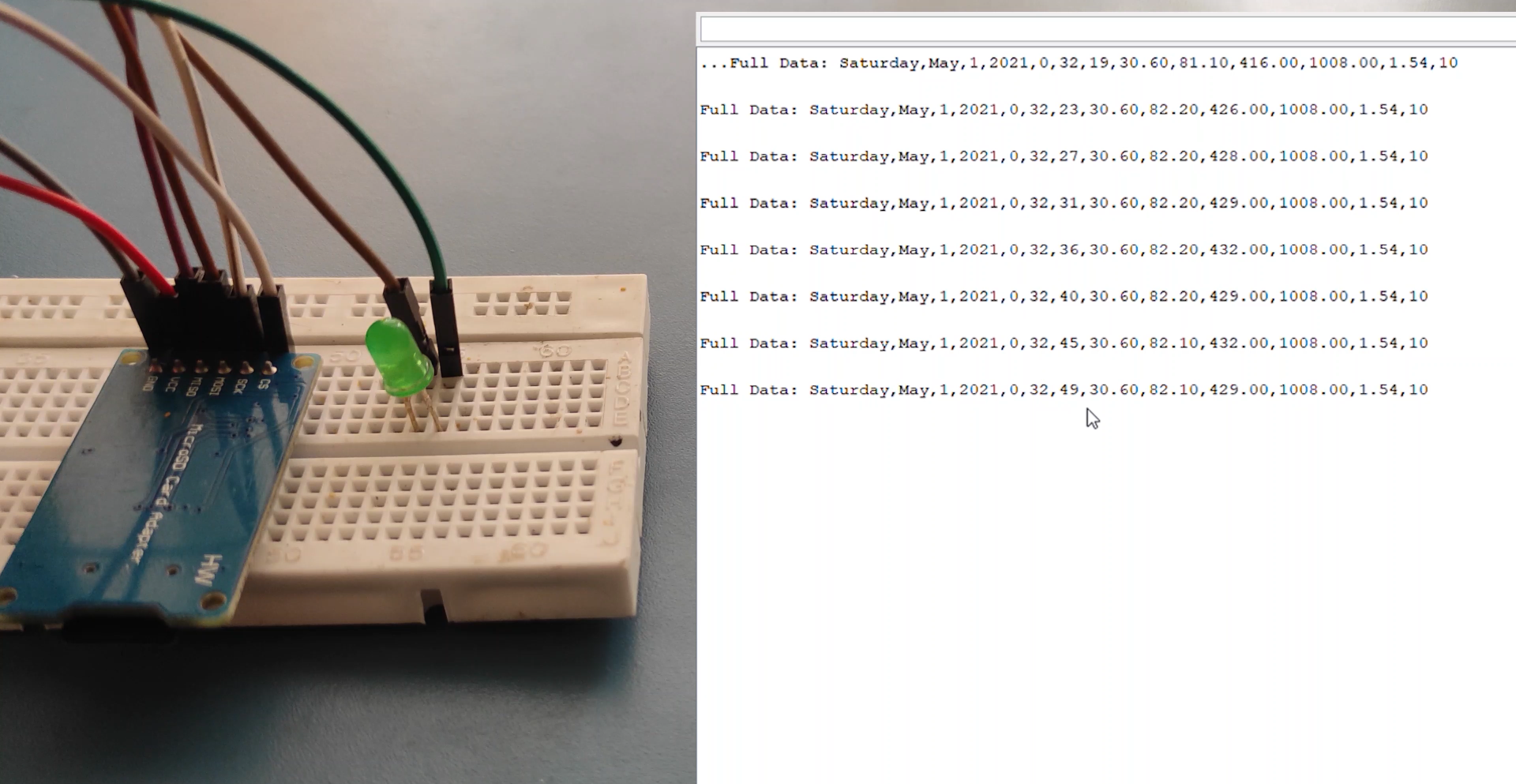
Now after uploading the code to the Arduino, if everything is ok, the following will appear on the serial monitor.

As we can see, the SD card has been successfully initialized, the writing to it has been successful as well, and also reading the written data or the string “Testing text 1, 2 ,3…” has been successful read. If we open the SD card on our computer we can see the created “test.txt” file and the written text in it.
Coding..
.png)
.png)
.png)
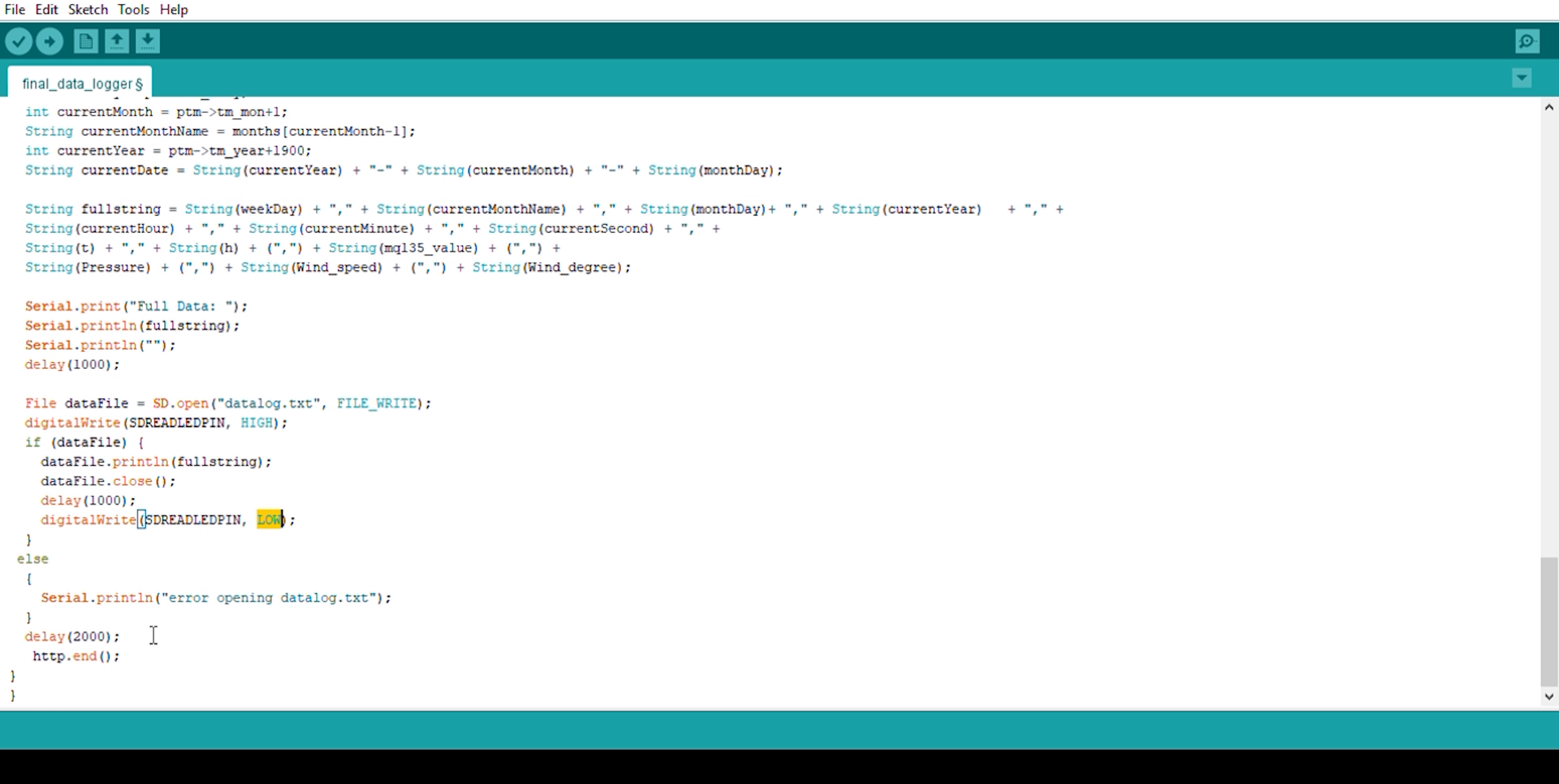
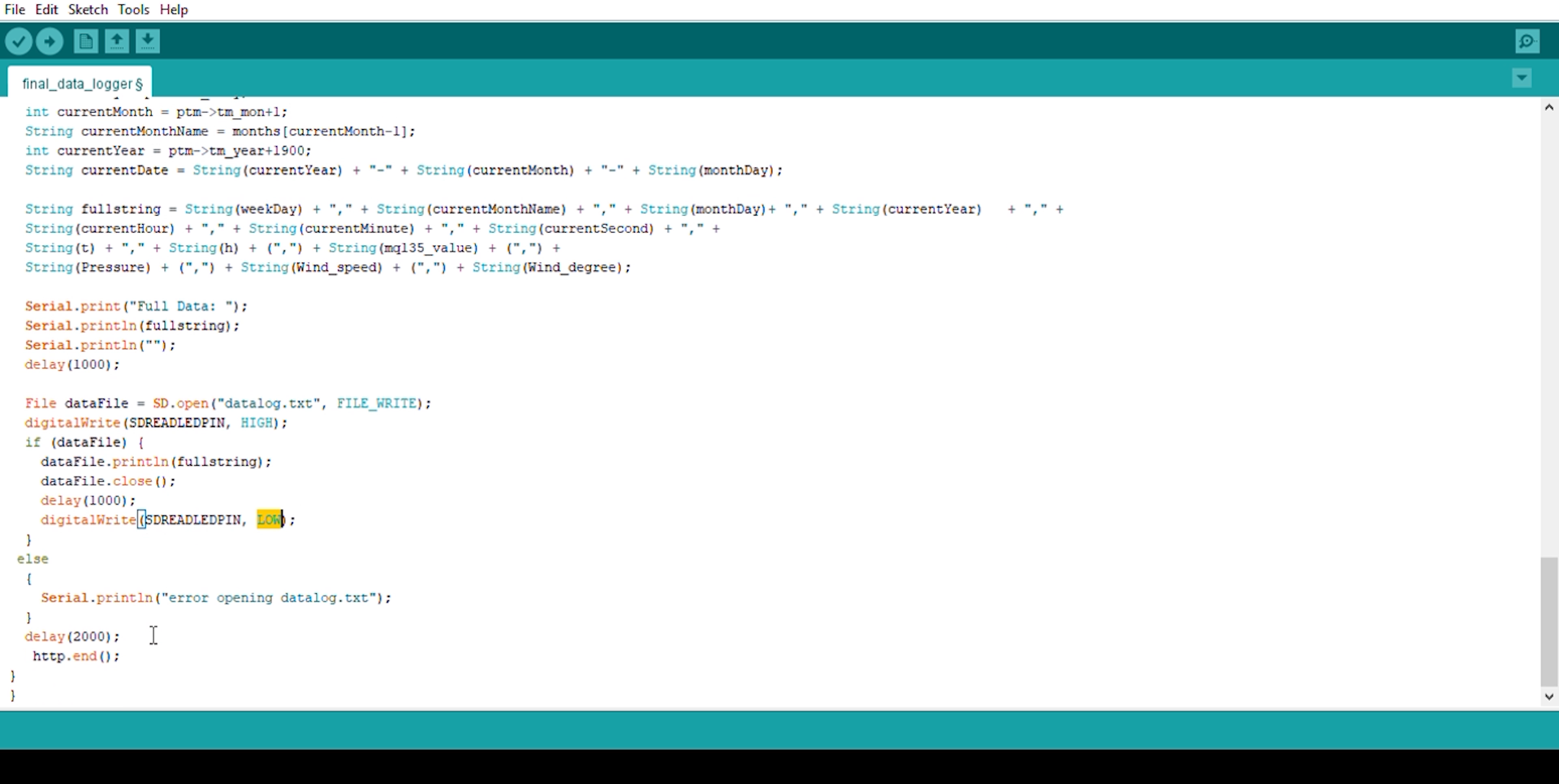
void Write_SDcard()
{
// open the file. note that only one file can be open at a time,
// so you have to close this one before opening another.
File dataFile = SD.open("LoggerCD.txt", FILE_WRITE);
// if the file is available, write to it:
if (dataFile) {
dataFile.print(rtc.getDateStr()); //Store date on SD card
dataFile.print(","); //Move to next column using a ","
dataFile.print(rtc.getTimeStr()); //Store date on SD card
dataFile.print(","); //Move to next column using a ","
dataFile.print(DHT.temperature); //Store date on SD card
dataFile.print(","); //Move to next column using a ","
dataFile.print(DHT.humidity); //Store date on SD card
dataFile.print(","); //Move to next column using a ","
dataFile.println(); //End of Row move to next row
dataFile.close(); //Close the file
}
else
Serial.println("OOPS!! SD card writing failed");
}
Arduino serial monitor can be opened by clicking on the magnifying glass icon on the upper right side of the IDE or under tools. The serial monitor is used mainly for interacting with the Arduino board using the computer, and is a great tool for real-time monitoring and debugging. In order to use the monitor, you’ll need to use the Serial class.
Debugging Arduino Code and Hardware
Unlike other software programming platforms, Arduino doesn’t have an onboard debugger. Users can either use third-party software, or they can utilize the serial monitor to print Arduino’s active processes for monitoring and debugging.
By using the Serial class, you can print to the serial monitor, debugging comments and values of variables. On most Arduino models, this will be using serial pins 0 and 1 which are connected to the USB port.
Code Structure
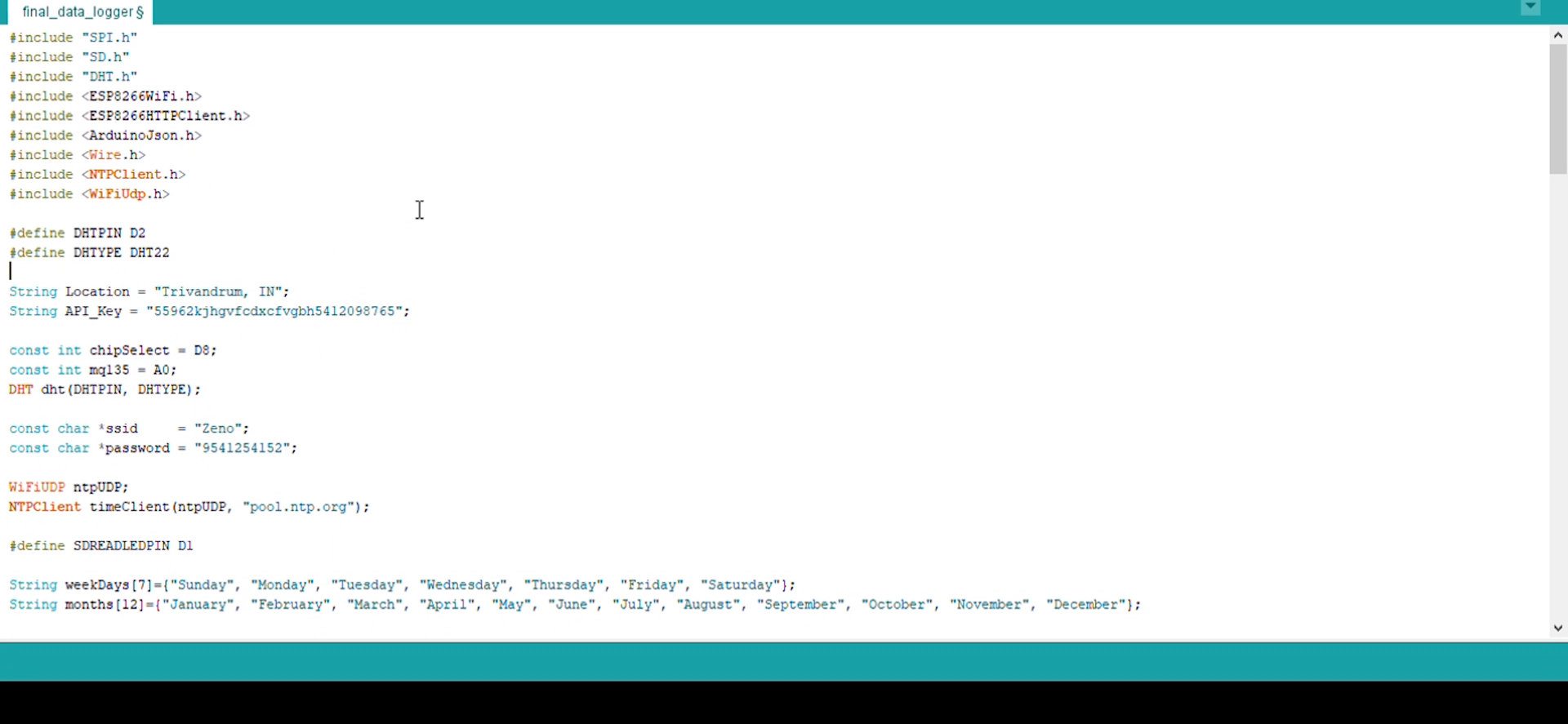
Libraries
In Arduino, much like other leading programming platforms, there are built-in libraries that provide basic functionality. In addition, it’s possible to import other libraries and expand the Arduino board capabilities and features. These libraries are roughly divided into libraries that interact with a specific component or those that implement new functions.
To import a new library, you need to go to Sketch > Import Library
Files
.png)
Arduino detailed code pls update the library with the arduino ide version to avoid confliction errors