Convert Video in Linux
FFmpeg is the best open-source video converter out there. It is plain, simple, but very powerful. FFmpeg is a command line program. There are a few graphical frontends too, but they tend to be buggy. So, the easiest way to convert video in Linux is using FFmpeg in the terminal (Linux command line).
Opening the Terminal
Terminal is in the applications menu in one of the sub-categories. (Depends on the distribution and the desktop environment). In Ubuntu, it is in Applications->Accessories->Terminal.
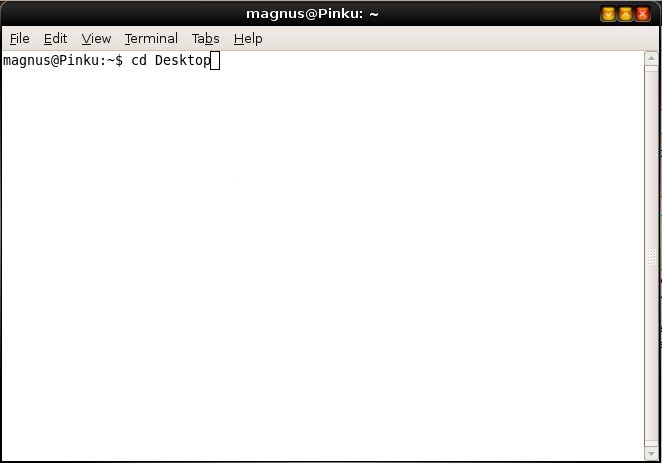
First, cd to the directory, where your video file is (cd means change directory)
If the file is on desktop, the command would be: cd Desktop
if it's in the videos folder, it would be: cd /home/$USER/Videos
Now you're virtually inside that folder.
First, cd to the directory, where your video file is (cd means change directory)
If the file is on desktop, the command would be: cd Desktop
if it's in the videos folder, it would be: cd /home/$USER/Videos
Now you're virtually inside that folder.
Converting Video
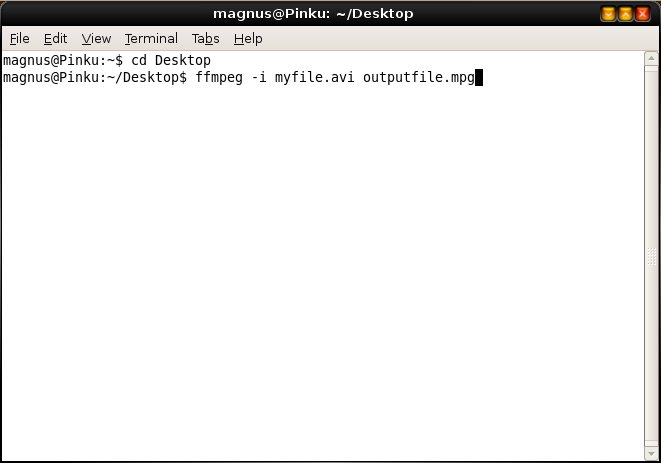
The basic command for converting video is: ffmpeg -i inputfile outputfile
The format of the output video comes from the file extension you specify on outputfile.
It can be any video format: flv, avi, mpg...
example: ffmpeg -i input.avi output.mpg
Now we start adding parameters.
parameters are options for converting video. they are in format: ffmpeg -i myfile.avi -parameter output.mpg
There are a number of parameters:
-ab -audio bitrate
-b -video bitrate
-sameq -produces same quality video, as the input
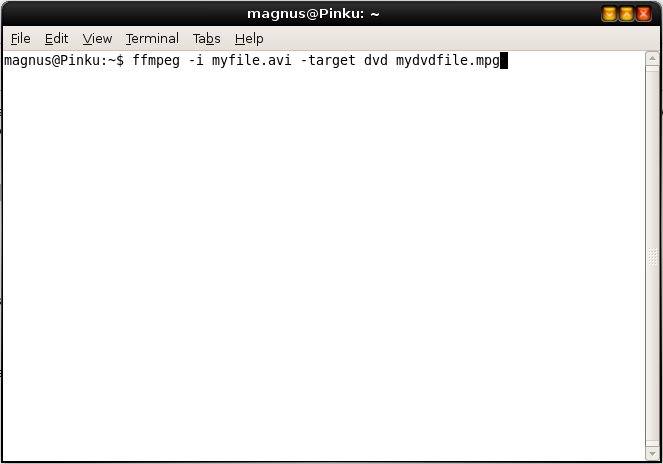
-target -target can be "vcd", "svcd", "dvd", "dv", "pal-vcd" or "ntsc-svcd".
example: ffmpeg -i myfile.avi -target ntsc-dvd mydvdfile.mpg
This makes a dvd video file
Examples:
I want to convert an mpg file to flv with 350 video bitrate and 64 audio bitrate:
ffmpeg -i mympgfile.mpg -b 350 -ab 64 myflvfile.flv
I want to convert an avi to mpg with the same quality:
ffmpeg -i avifile.avi -sameq output.mpg
Here is a great tutorial on this:
http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/8517
The format of the output video comes from the file extension you specify on outputfile.
It can be any video format: flv, avi, mpg...
example: ffmpeg -i input.avi output.mpg
Now we start adding parameters.
parameters are options for converting video. they are in format: ffmpeg -i myfile.avi -parameter output.mpg
There are a number of parameters:
-ab -audio bitrate
-b -video bitrate
-sameq -produces same quality video, as the input
-target -target can be "vcd", "svcd", "dvd", "dv", "pal-vcd" or "ntsc-svcd".
example: ffmpeg -i myfile.avi -target ntsc-dvd mydvdfile.mpg
This makes a dvd video file
Examples:
I want to convert an mpg file to flv with 350 video bitrate and 64 audio bitrate:
ffmpeg -i mympgfile.mpg -b 350 -ab 64 myflvfile.flv
I want to convert an avi to mpg with the same quality:
ffmpeg -i avifile.avi -sameq output.mpg
Here is a great tutorial on this:
http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/8517