Connect Your Siemens SIMATIC IOT2000 to Ubidots Using Node-RED
by UbiMaker in Circuits > Electronics
3572 Views, 5 Favorites, 0 Comments
Connect Your Siemens SIMATIC IOT2000 to Ubidots Using Node-RED

The reliability is a Siemens standard but now they have simplicity with the SIMATIC IOT2000 series. The industrial gateway of choice in factories and institutions exploring the SIMATIC IOT2000 series harmonizes, analyzes, and forwards data efficiently with common protocols like MQTT and Modbus. Based on a Yocto Linux, the SIMATIC IOT2000 series includes the IoT2020 and IoT2040 models which can manage its own automation systems. This incredible gateway harmonizes the communication between various data sources effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments, analyses it, and forwards it to the corresponding recipients, offering a solution that can be easily implemented and perfect for retrofitting.
Available in two versions, the IoT 2020 designed for educational institutions and public spaces while the IoT 2040 is optimized for Industrial environments. If you'd like to learn more check out the SIMATIC IOT 2000 support and forums.
In this guide we detail the integration of the Siemens SIMATIC IOT 2000 with Ubidots, using an external device serial communicated through RS-485 interface with the SIMATIC IOT 2000 and configuring a flow in Node-RED to transmit the data obtained to Ubidots over MQTT.
Requirements
- Ethernet cable
- SD Card
- 24V power supply
- Siemens SIMATIC IOT 2000
- Arduino UNO
- Arduino Grove Shield
- RS485 Shield for Arduino
Ubidots account - or - STEM License
Setting Up the SIMATIC IOT2000
First, you must register with or have access to Siemens Support Portal to download all initial configurations. This Portal will also provide troubleshooting and support from Siemens on any hardware related inquires. The entire IOT2000 series is setup the same way, please follow this tutorial for any devices in the series.
Setup:
I. Burn and Install the SD-Card
II. First commissioning of the SIMATIC IOT2000
III. Hardware Setup IV. Visualizing your data in Ubidots
I: Burn and Install the SD-Card

1. Begin by burning the SD-Card with the image provided by the Siemens Industry Online Support page. Please, download and save Example_Image_V2.1.3 for later.
2. Insert the microSD-Card into the SD-Card slot of your computer (an adaptor may be needed).
3. Unzip the downloaded image and burn it to the SD-Card. Microsoft users click here for how to burn images to your SD-Card. Linux users please continue reading.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Make sure the SD-Card is formatted before burn the image into it.
- Linux:
1. Open your computer terminal and go to the folder where the zip file was. downloaded using the cd command. e.i: I downloaded the file into the "Downloads" directory:
cd Downloads
2. Unzip the downloaded file running the command below:
sudo unzip 109741799_Example_Image_V2.1.3.zip
Once the zip file was properly unzipped you will see a file named example-V2.1.3.wic as is shown above.
NOTE: If you get an error running the command above verify if the name of the file downloaded is the same one, if not replace it with the correct one.
3. Verify the location of the SD-card to unmount it and burn the image. Run the command below to verify the location:
df -h
The SD-card should be located it the directory /dev/...; in my case the sd card is located in the following directory /dev/mmcblk0
4. Umount the SD-Card running the command below:
umount /dev/mmcblk0
5. To burn the image, replace the name of the file unzipped and the location of the SD-Card; the structure of the command is as follows:
sudo dd bs=1M if={name_of_the_image} of={SD_location}
Once the parameters are replaced with the correct ones, the command should look similar to the following:
sudo dd bs=1M if=example-V2.1.3.wic of=/dev/mmcblk0
NOTE: Running this command make take a couple minutes, please be patient :)
Install your SD-Card
Connect your SD-Card into your hardware. Below we have installed the SD-Card into the SIMATIC 2040 where indicated.
II: First Commissioning of the SIMATIC IOT2000
The following steps show how to access the SIMATIC IOT2040 using the static IP to setup the gateway's network. At this point is important to mention that the SIMATIC IOT 2040 brings DHCP Address by default in the Ethernet Port - X2P1, if your desire you can access directly using the IP address assigned.
1. Power off and Connect one end of the Ethernet Cable to your computer and the other to the Ethernet Port- X1P1 of the SIMATIC IOT2000 device.
CAUTION: Only use a DC 9...36V power supply!
2. Once the SIMATIC IOT2000 is powered on, you will see the following behavior on the LEDs of the gateway:
- PWR: Solid; device turned ON
- SD: Intermittent.... then Solid turned OFF
- USB: Solid; device turned ON
The SD LED will be intermittent because is resizing the SD card with the image, wait until the SD LED change it status to Solid turned OFF to access to the gateway.
3. The SIMATIC IOT2000 lets you access to via Serial, SSH or Telnet; this guide uses the SSH connection.
The SIMATIC IOT2000 has a static IP address by default -> 192.168.200.1 . To establish a SSH connection, your computer have the same subnet as the SIMATIC IOT2000.
If you are working with Microsoft, please reference this getting started guide for how to access the gateway. Linux users please continue with the following steps.
4. Once the network of your computer is configured on the same subnet of the SIMATIC IOT2000, verify its connectivity with a ping:
ping 192.168.200.1
expected result:
PING 192.168.200.1 (192.168.200.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.200.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.04 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.03 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.00 ms
If you receive the expected result the SIMATIC IOT2000 is properly connected.
5. Access to the gateway running the command below:
ssh root@192.168.200.1
Upon first accessing the Gateway you will be prompted to approve the security message. Send the command yes and press enter to approve and continue. Once access is properly established you will see the following root in your terminal:
root@iot2000:~#
6. As mentioned above, the static IP address of the SIMATIC IOT2000 is set to 192.168.200.1 . Thus, if another static IP address or DHCP address is required, this can be set in the "interfaces" file in the "/etc/network" directory.
To do this, enter to the directory specified with the command below:
cd /etc/network/
Open the interfaces file using nano editor running the following command:
nano interfaces
The content of the interfaces file by default be the same as below:
# /etc/network/interfaces -- configuration file for ifup(8), ifdown(8)
# The loopback interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# Wired interfaces
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.200.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet dhcp
As mentioned above, If you are working with the SIMATIC IOT2040 the DHCP Address is configure by default on the second port (X2 P1LAN). Ensure your Ethernet cable is connected to the second Ethernet port and reboot the gateway.
If you are working with the SIMATIC IOT2020 and desire to setup DHCP Address, you must modify the interfaces file as is shown below, then reboot the gateway:
# /etc/network/interfaces -- configuration file for ifup(8), ifdown(8)
# The loopback interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# Wired interfaces
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
Once the DHCP Address is configured you can use a network scanner app to know the new ip address assigned to the SIMATIC 2000, we highly recommend you use fing which is easy to use and is available in both Google's Play Store and Apple's App Store. :)
III. Hardware Setup
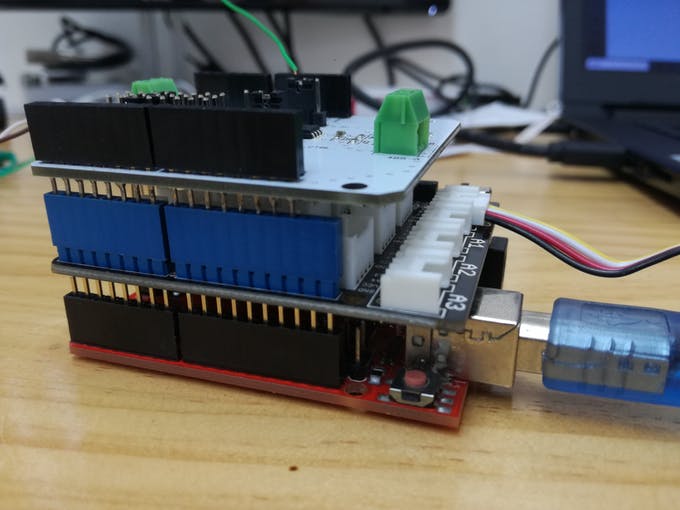
SIMATIC IOT2000 with Arduino (external device)
Based on your environment and technical requirements, choose the best device to complete your project. Make sure you device is transmitting data through RS485.
Our project calls for a Arduino UNO using a RS485 shield with an humidity sensor to transmit it values to Ubidots.
- Hardware Setup:
Fly-out Rule: To avoid any hardware issue please make sure that the SIEMENS IOT2000 is turned OFF before make the connections:
Arduino connections
1. First attach the Arduino Grove Shield to the Arduino UNO and then attach the RS485 shield.
2. Connect the Humidity Sensor to A0 pinout of the Grove Shield using a grove cable. Once everything is properly attached your Arduino will look similar to above.
3. Verify if the headers of the RS485 shield are properly assigned with the configuration below:
- P1 -> 5V
- P2 -> TX_CTRL
- D2 -> TX
- D3 -> RX
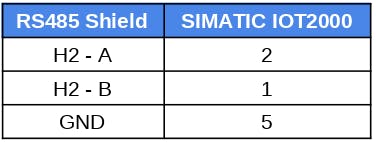
RS485 connections:
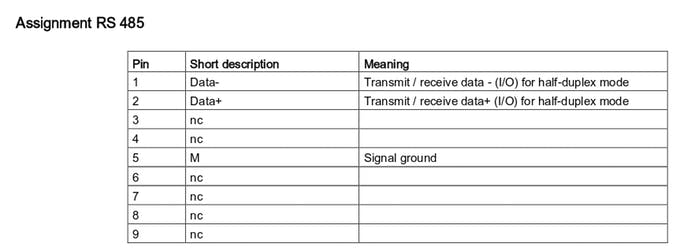
Click here for more detailed information about the SIMATIC IOT 2000 operating instructions
iot2000_operating_instructions_e_en-US.pdf
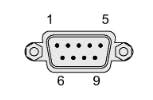
1. The X30 COM and X31 COM allow you work with RS232/RS422/RS485 interfaces; in this case we are going to work with the X30 COM - RS485. See the images above to see the Connector Pinout
2. Follow the table above to make the connection between the Arduino RS485 shield and the SIMATIC IOT2000.
Firmware Upload:
1. Open Arduino IDE.
2. Select the Arduino UNO from Tools > Board menu
3. Connect the Arduino UNO to your computer and select the port COM assigned from Tools > Port > Arduino UNO.
4. Now with everything configured, copy and paste this code in the Arduino IDE.
5. Verify and upload the code choosing the "check mark" icon and then the "right-arrow" icon beside the check mark icon.
Now your Arduino UNO is sending data to the Siemens SIMATIC IOT 2000 properly.
SIMATIC IOT2000 With Node-RED
Before starting with the Node-RED flow, we must establish some configurations in the SIMATIC IOT2000. Please, follow the steps below carefully to ensure the right functionality:
Package manager:
Go to the opkg directory:
cd /etc/opkg
2. Edit the opkg.conf file adding the lines below at the end of the file:
src iotdk-all http://iotdk.intel.com/repos/2.0/iotdk/all
src iotdk-i586 http://iotdk.intel.com/repos/2.0/iotdk/all
src iotdk-quark http://iotdk.intel.com/repos/2.0/iotdk/all
src iotdk-x86 http://iotdk.intel.com/repos/2.0/iotdk/all
3. Next, edit the arch.conf file adding the lines below at the end of the file:
arch i586 12
arch quark 13
arch x86 14
4. Update the configurations made with:
opkg update
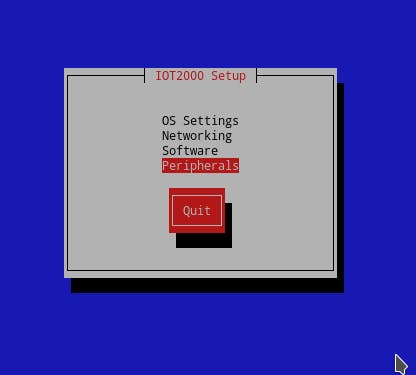
5. Write iot2000setup to open the setup interface and configure the X30 COM as RS-485. To do this, select Peripherals > Configure External COM Port > X30 > RS485.
6. Assign the baud-rate to the port with the command below:
stty -F /dev/ttyS2 9600
7. Reboot the SIMATIC to save the changes with the command reboot.
Node-RED:
1. Write the command below "in your computer's terminal" to enter to the Node-RED directory:
cd /usr/lib/node_modules/
2. Then, install the node required by writing the following command:
npm install -g node-red-contrib-modbus
This process will take a couple of minutes so please be patient.
NOTE: If you get an issue installing the node, see the following tips and tricks to troubleshoot. 3. To start Node-RED type the command below:
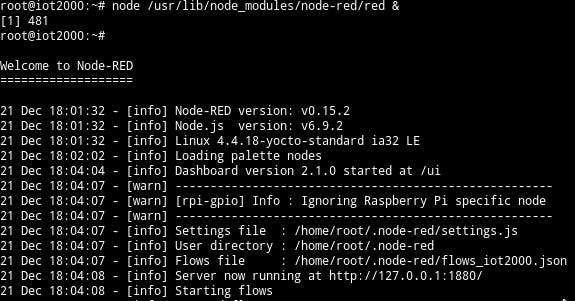
node /usr/lib/node_modules/node-red/red &
Once the Node-RED started properly, you should see the behavior above in your SIMATIC IOT2000, this will take a couple of minutes.
3. Once the Node-RED is started, open a web-browser (firefox, preferably) and write the IP Address of the SIMATIC IOT2000 and the port 1880 (i.e http://192.168.200.1:1880) to open the Node-RED web interface
4. Now click on Node-RED menu in the upper right corner, then “Import” -> “Clipboard” and paste the code below:
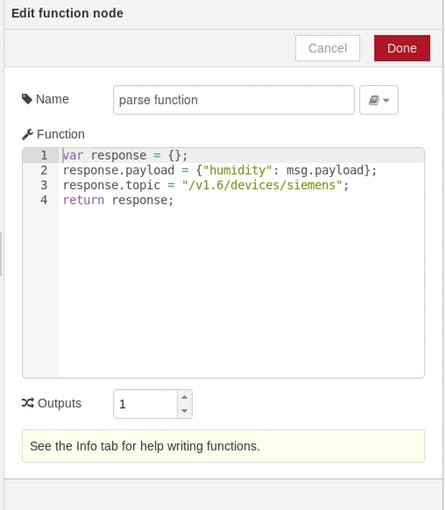
[{"id":"38e1405b.5796d","type":"serial in","z":"c88a5f47.16d498","name":"rs-485","serial":"8bf5451a.2fb14","x":170.5,"y":223,"wires":[["f7937636.d26448","ae2f3a52.32f23"]]},{"id":"f7937636.d26448","type":"debug","z":"c88a5f47.16d498","name":"","active":true,"console":"false","complete":"false","x":377.5,"y":121,"wires":[]},{"id":"ae2f3a52.32f23","type":"function","z":"c88a5f47.16d498","name":"parse function","func":"var response = {};\nresponse.payload = {\"humidity\": msg.payload};\nresponse.topic = \"/v1.6/devices/siemens\";\nreturn response;","outputs":1,"noerr":0,"x":374.5,"y":223,"wires":[["51bcbd87.0af04c"]]},{"id":"51bcbd87.0af04c","type":"mqtt out","z":"c88a5f47.16d498","name":"","topic":"","qos":"","retain":"","broker":"cefb900f.f02ca8","x":605.5,"y":222,"wires":[]},{"id":"8bf5451a.2fb14","type":"serial-port","z":"","serialport":"/dev/ttyS2","serialbaud":"9600","databits":"8","parity":"none","stopbits":"1","newline":"\\n","bin":"false","out":"char","addchar":false},{"id":"cefb900f.f02ca8","type":"mqtt-broker","z":"","broker":"things.ubidots.com","port":"1883","clientid":"","usetls":false,"compatmode":true,"keepalive":"60","cleansession":true,"willTopic":"","willQos":"0","willPayload":"","birthTopic":"","birthQos":"0","birthPayload":""}]
5. Assign your Ubidots TOKEN as username in the security tab of the MQTT-broker node. If you don't know how to get your Ubidots TOKEN see this guide.
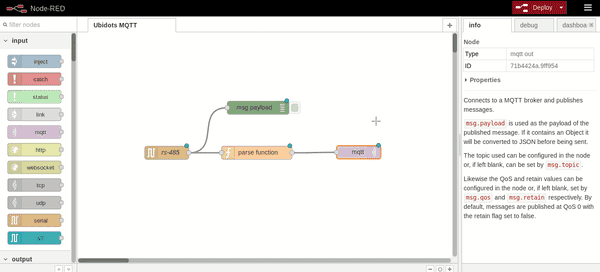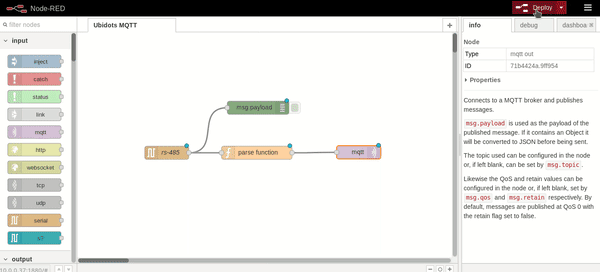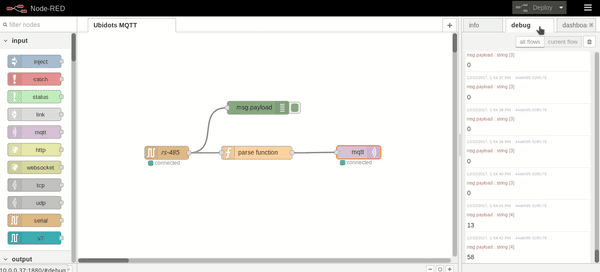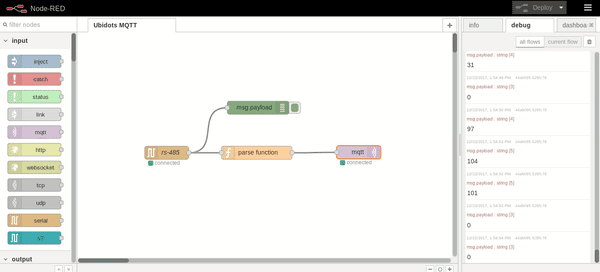
Once the Ubidots TOKEN is assigned, press Deploy and the status of the serial and mqtt node should appear as connected. Also, if you wish to visualize the sensor value received, just press the debug tab:
IV. Visualizing Your Data in Ubidots
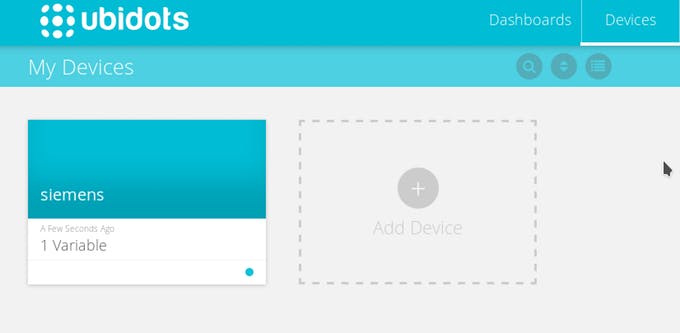
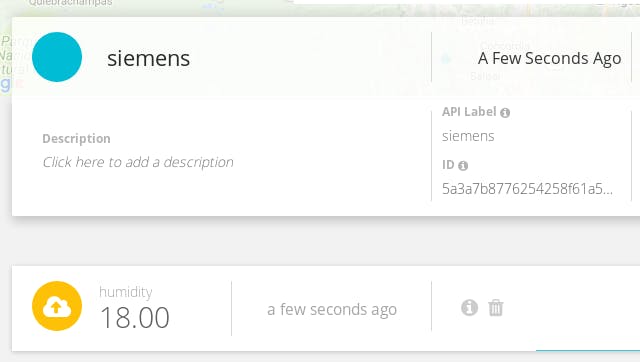
Go to the device section of your Ubidots account and see a new device created. Then, enter to the device and you will see the variable created with the real-time data of the sensor connected.
If your desire to modify the name of the device and the variables, edit the parse function created in the Node-RED flow.
Results
In what felt like too easy of a process for hardware, we just integrated the SIMATIC IOT2000. We built this integration with starter equipment and simple know-how, with the right devices for your environment, you will be able to launch industrial applications in a matter of days instead of months.
Now its time to create Ubidots Dashboards to visualize and interpret your data to control and monitoring your machines and environments remotely and keeping your clients happy and productions at its peak.