Simple Brightness Indicator and Alert Using LDR, Arduino, Python.
by sbhat8 in Circuits > Microcontrollers
13675 Views, 16 Favorites, 0 Comments
Simple Brightness Indicator and Alert Using LDR, Arduino, Python.
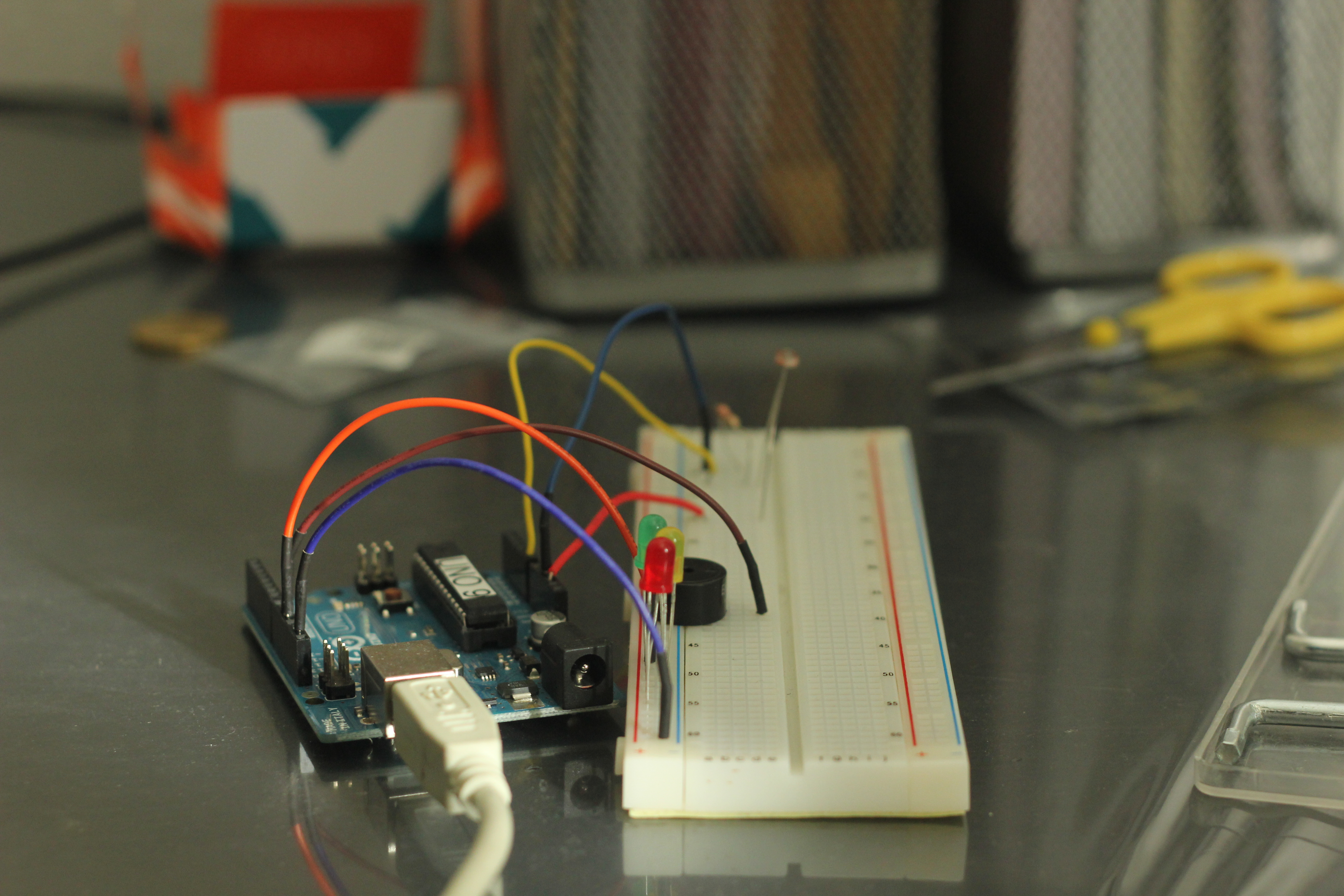
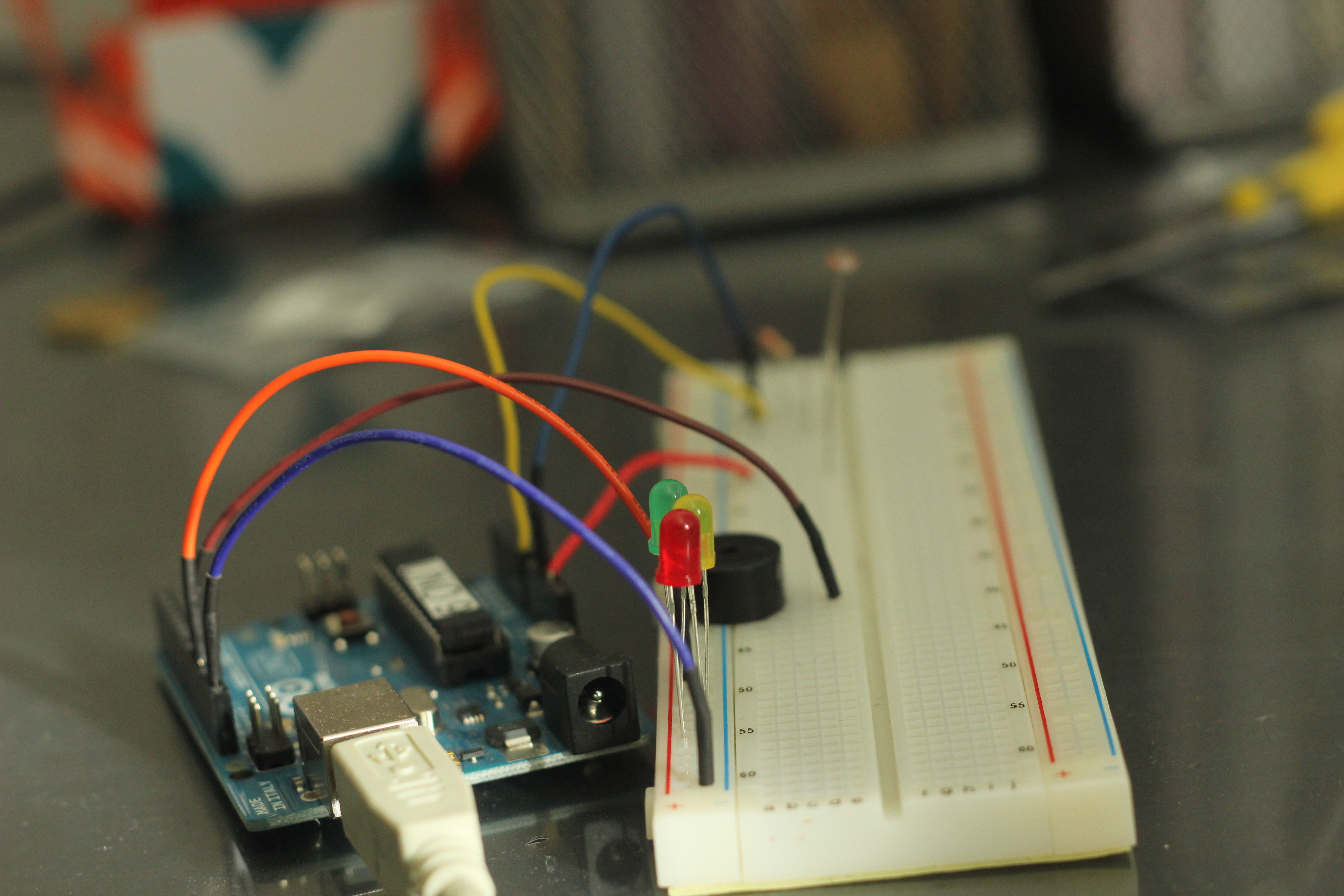
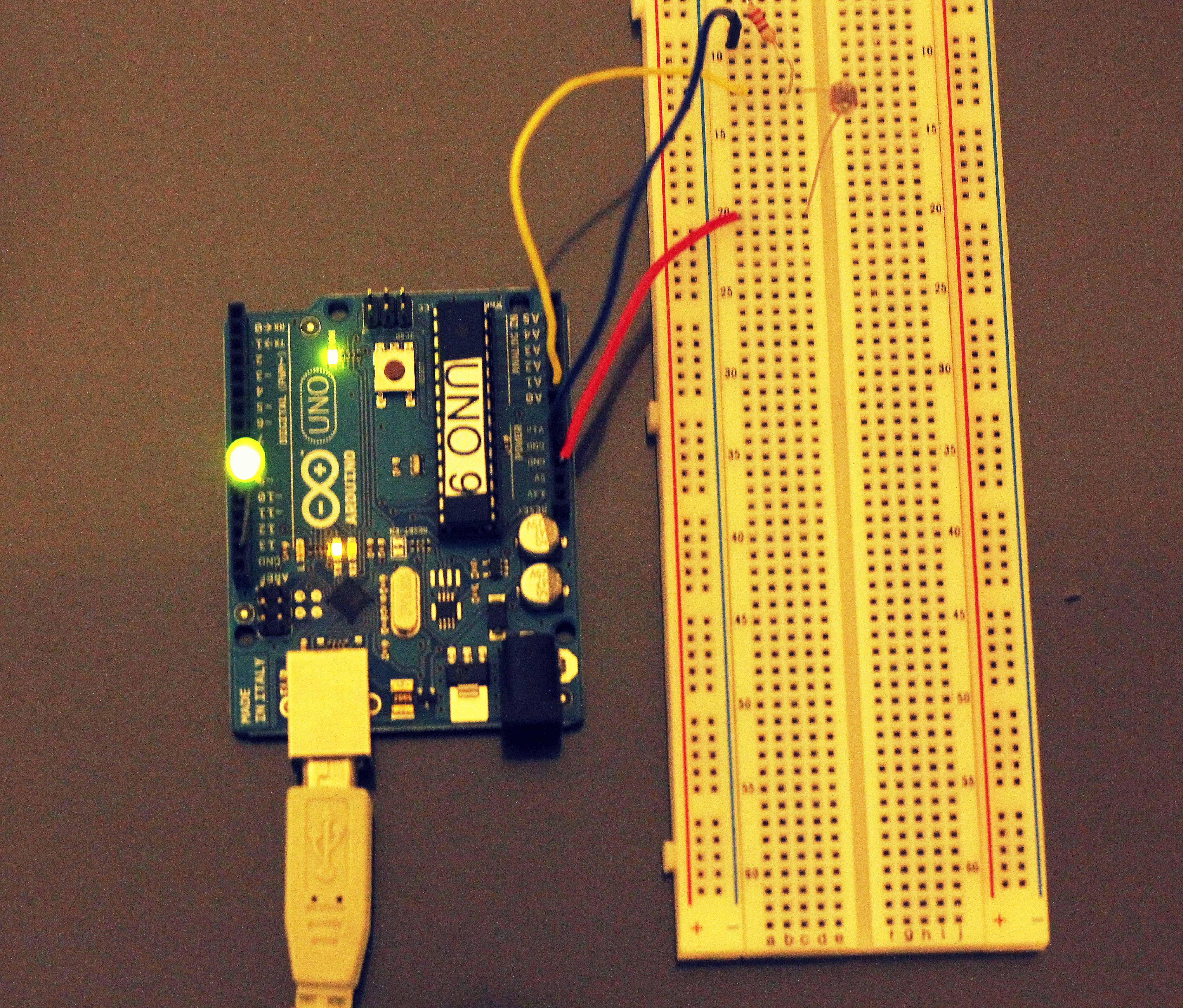
Project uses LDR (Light dependent Resistor) to change the resistance across the circuit which can be used to control the behavior of different components.
In this project I am using LED and Speaker as the output components which detects the brightness in the room and alerts the user that Lights may be on. This can be extended to various applications like Home Automation, fun project to play different music when user passes by.
In this project I am using LED and Speaker as the output components which detects the brightness in the room and alerts the user that Lights may be on. This can be extended to various applications like Home Automation, fun project to play different music when user passes by.
Collect Arduino and Components
Components used:
• Arduino Uno
• LDR
• Resistors(I am using 330 Ohms)
• Breadboard
• Speaker (EXULIT 1196)
• LED lights
• Connecting Wires
• Arduino Uno
• LDR
• Resistors(I am using 330 Ohms)
• Breadboard
• Speaker (EXULIT 1196)
• LED lights
• Connecting Wires
Connect Them According to the Circuit Diagram
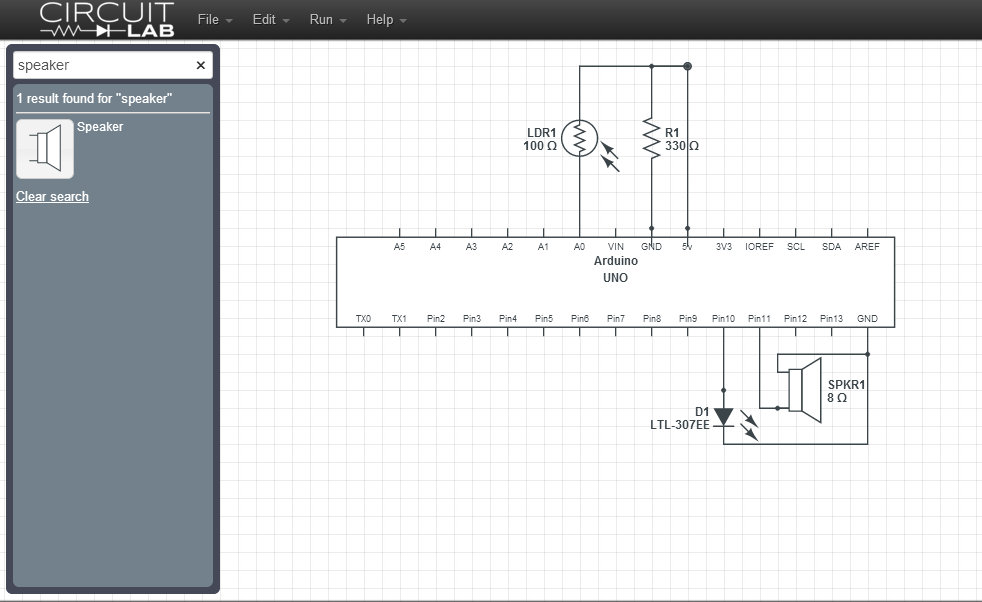
As shown in Circuit diagram, connect LDR to A0 and Resistor connected to GND and 5V
Output components LED and Speaker are connected to pin 10, pin 11.
Output components LED and Speaker are connected to pin 10, pin 11.
Write Code in Arduino and Connect to the USB.
Open Arduino IDE, Depending on the values you get in Serial(Depends on the brightness in the room)
int inputPin = 0; //Pin for Photo resistor
int outputPin=11; //Pin for LED
int outputPin1=10;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Begin serial communcation
pinMode( outputPin, OUTPUT );
}
void loop()
{
Serial.println(analogRead(inputPin));
int reading = analogRead(inputPin);
if(reading > 90) { //Value here depends on the brightness of the room and how you want to calibrate it.
analogWrite(outputPin1, analogRead(inputPin));
analogWrite(outputPin, analogRead(inputPin) );
} else {
analogWrite(outputPin1, 0);
analogWrite(outputPin, 0);
}
}
int inputPin = 0; //Pin for Photo resistor
int outputPin=11; //Pin for LED
int outputPin1=10;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Begin serial communcation
pinMode( outputPin, OUTPUT );
}
void loop()
{
Serial.println(analogRead(inputPin));
int reading = analogRead(inputPin);
if(reading > 90) { //Value here depends on the brightness of the room and how you want to calibrate it.
analogWrite(outputPin1, analogRead(inputPin));
analogWrite(outputPin, analogRead(inputPin) );
} else {
analogWrite(outputPin1, 0);
analogWrite(outputPin, 0);
}
}
Write Python Code to Read Serial Data
To save serial data to file system using Python. Use below code:
# Python code starts.
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('COM3', 9600) //COM3 is the serial port name you connect your Arduino to, It might be different for differnt user
f = open("LDR.txt", "w")
while True:
f.write(ser.readline())
#Python code ends
# Python code starts.
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('COM3', 9600) //COM3 is the serial port name you connect your Arduino to, It might be different for differnt user
f = open("LDR.txt", "w")
while True:
f.write(ser.readline())
#Python code ends
Use Matplot Lib to Make a Graph Out of It.
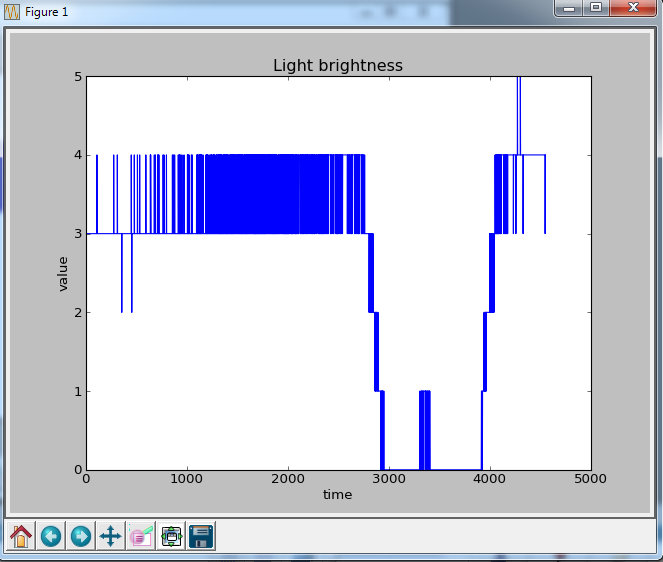
#!/usr/bin/python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
with open("LDR.txt") as f:
data = f.read()
data = data.split('\n')
x = [row.split(' ')[0] for row in data]
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax1.set_title("Light brightness")
ax1.set_xlabel('time')
ax1.set_ylabel('value')
lines = [i for i in open("LDR.txt") if i[:-1]]
ax1.plot(map(int, lines), 'b-')
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
with open("LDR.txt") as f:
data = f.read()
data = data.split('\n')
x = [row.split(' ')[0] for row in data]
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax1.set_title("Light brightness")
ax1.set_xlabel('time')
ax1.set_ylabel('value')
lines = [i for i in open("LDR.txt") if i[:-1]]
ax1.plot(map(int, lines), 'b-')
plt.show()